Early detection versus primary prevention in the PLCO flexible sigmoidoscopy screening trial: Which has the greatest impact on mortality?
- PMID: 28976536
- PMCID: PMC5716922
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.31034
Early detection versus primary prevention in the PLCO flexible sigmoidoscopy screening trial: Which has the greatest impact on mortality?
Abstract
Background: Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) with flexible sigmoidoscopy (FS) has been shown to reduce CRC mortality. The current study examined whether the observed mortality reduction was due primarily to the prevention of incident CRC via removal of adenomatous polyps or to the early detection of cancer and improved survival.
Methods: The Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) cancer screening trial randomized 154,900 men and women aged 55 to 74 years. Individuals underwent FS screening at baseline and at 3 or 5 years versus usual care. CRC-specific survival was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier curves and proportional hazards modeling. The authors estimated the percentage of CRC deaths averted by early detection versus primary prevention using a model that applied intervention arm survival rates to CRC cases in the usual-care arm and vice versa.
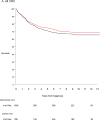
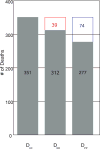
Results: A total of 1008 cases of CRC in the intervention arm and 1291 cases of CRC in the usual-care arm were observed. Through 13 years of follow-up, there was no significant difference noted between the trial arms with regard to CRC-specific survival for all CRC (68% in the intervention arm vs 65% in the usual-care arm; P =.16) or proximal CRC (68% vs 62%, respectively; P = .11) cases; however, survival in distal CRC cases was found to be higher in the intervention arm compared with the usual-care arm (77% vs 66%; P<.0001). Within each arm, symptom-detected cases had significantly worse survival compared with screen-detected cases. Overall, approximately 29% to 35% of averted CRC deaths were estimated to be due to early detection and 65% to 71% were estimated to be due to primary prevention.
Conclusions: CRC-specific survival was similar across arms in the PLCO trial, suggesting a limited role for early detection in preventing CRC deaths. Modeling suggested that approximately two-thirds of avoided deaths were due to primary prevention. Future CRC screening guidelines should emphasize primary prevention via the identification and removal of precursor lesions. Cancer 2017;123:4815-22. © 2017 American Cancer Society.
Keywords: PLCO; Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial; colorectal cancer; early detection; flexible sigmoidoscopy; screening.
© 2017 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Comment in
-
Early detection versus prevention in colorectal cancer screening: Methods estimates and public health implications.Cancer. 2017 Dec 15;123(24):4767-4769. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31032. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28976554 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Segnan N, Armaroli P, Bonelli L, et al. Once-only sigmoidoscopy in colorectal cancer screening: follow-up findings of the Italian Randomized Controlled Trial–SCORE. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1310–1322. - PubMed
-
- Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, et al. Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;375:1624–1633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

