Reference ranges for serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in healthy Chinese adults
- PMID: 28976993
- PMCID: PMC5627923
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185561
Reference ranges for serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in healthy Chinese adults
Abstract
Purpose: To determine serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-I) levels in healthy Chinese adults, establish reference ranges for serum IGF-I levels and observe the effects of age, sex, body mass index (BMI) and geographical region on serum IGF-I levels.
Methods: In total, 2791 healthy adults (1339 males and 1452 females) from the north (Beijing) and south (Guizhou Province) of China were recruited following a questionnaire survey, physical examination and laboratory examination. Both sexes were divided into 13 groups according to age (18, 19, 20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, 40-44, 45-49, 50-54, 55-59, 60-64, 65-69 and ≥70 years). The serum IGF-I levels were measured by performing a chemiluminescent assay (Immulite 2000®), and the LMS (Lambda-Mu-Sigma) method was applied to construct smooth centile curves of age-specific IGF-I levels.
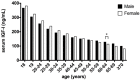
Results: Serum IGF-I levels in the adults gradually decreased with increasing age from 18 to 70 years in both the male and female participants. Although the decrease in the level of IGF-1 was more pronounced in females than in males, no significant difference was observed between the sexes, except in the 60- to 64-year-old age group (P = 0.0329). The multiple linear regression model showed that there was an inverse relationship between the serum IGF-I level and BMI (P<0.001), and the serum IGF-I level in the Guizhou population was higher than that in the Beijing population (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The normal reference ranges for age- and sex-specific serum IGF-I levels were established for the first time in a large sample of Chinese adults. The serum IGF-I levels were significantly influenced by age, BMI and geographical region.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

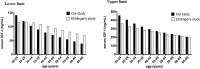
References
-
- Salmon wd, Daughaday wh. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J Lab Clin. Med. 1957;49(6):825–836. - PubMed
-
- Rinderknecht E, Humbel RE. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253(8):2769–2776. - PubMed
-
- Isojima T, Shimatsu A, Yokoya S, Chihara K, Tanaka T, Hizuka N, et al. Standardized centile curves and reference intervals of serum insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) levels in a normal Japanese population using the LMS method. Endocr. J. 2012;59: 771–780. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ12-0110 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cook DM, Yuen KCJ, Biller BMK, Kemp SF, Vance ML. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for growth hormone use in growth hormone-deficient adults and transition patients—2009 update: executive summary of recommendations. Endocr. Pract. 2009, 15(6):580–586. doi: 10.4158/EP.15.6.580 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Juul A, Bang P., Hertel N.T., Main K, Dalgaard P., Jorgensen K., et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I in 1030 healthy children, adolescents, and adults: relation to age, sex, stage of puberty, testicular size, and body mass index. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, 1994;78: 744–752. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.3.8126152 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

