Safe prone checklist: construction and implementation of a tool for performing the prone maneuver
- PMID: 28977254
- PMCID: PMC5496747
- DOI: 10.5935/0103-507X.20170023
Safe prone checklist: construction and implementation of a tool for performing the prone maneuver
Abstract
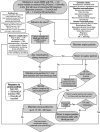
Objective: To construct and implement an instrument (checklist) to improve safety when performing the prone maneuver.
Methods: This was an applied, qualitative and descriptive study. The instrument was developed based on a broad review of the literature pertaining to the construction of a care protocol using the main electronic databases (MEDLINE, LILACS and Cochrane).
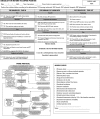
Results: We describe the construction of a patient safety tool with numerous modifications and adaptations based on the observations of the multidisciplinary team regarding its use in daily practice.
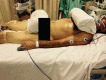
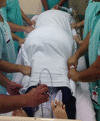
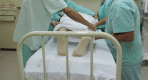
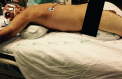
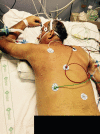
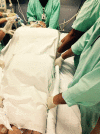
Conclusion: The use of the checklist when performing the prone maneuver increased the safety and reliability of the procedure. The team's understanding of the tool's importance to patient safety and training in its use are necessary for its success.
Objetivo: Construir e implementar um instrumento (checklist) para melhoria do cuidado na manobra prona.
Métodos: Estudo aplicativo, qualitativo e descritivo. O instrumento foi desenvolvido a partir de ampla revisão da literatura, para construção de um protocolo de atendimento assistencial, utilizando as principais bases eletrônicas (MEDLINE, LILACS e Cochrane).
Resultados: Descrevemos a construção de uma ferramenta de segurança do paciente com suas inúmeras modificações e adaptações, a partir das observações da equipe multidisciplinar com seu uso na prática diária.
Conclusão: A aplicação do checklist na manobra de prona acrescentou confiabilidade e segurança ao procedimento. O entendimento da importância da ferramenta na segurança do paciente, por parte da equipe, e sua capacitação são necessários para seu sucesso.
Objetivo: Construir e implementar um instrumento (checklist) para melhoria do cuidado na manobra prona.
Métodos: Estudo aplicativo, qualitativo e descritivo. O instrumento foi desenvolvido a partir de ampla revisão da literatura, para construção de um protocolo de atendimento assistencial, utilizando as principais bases eletrônicas (MEDLINE, LILACS e Cochrane).
Resultados: Descrevemos a construção de uma ferramenta de segurança do paciente com suas inúmeras modificações e adaptações, a partir das observações da equipe multidisciplinar com seu uso na prática diária.
Conclusão: A aplicação do checklist na manobra de prona acrescentou confiabilidade e segurança ao procedimento. O entendimento da importância da ferramenta na segurança do paciente, por parte da equipe, e sua capacitação são necessários para seu sucesso.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bryan AC. Conference on the scientific basis of respiratory therapy. Pulmonary physiotherapy in the pediatric age group. Comments of a devil´s advocate. Pt 2Am Rev Resp Dis. 1974;110(6):143–144. - PubMed
-
- Taccone P, Pesenti A, Latini R, Polli F, Vagginelli F, Mietto C, Caspani L, Raimondi F, Bordone G, Iapichino G, Mancebo J, Guérin C, Ayzac L, Blanch L, Fumagalli R, Tognoni G, Gattinoni L, Prone Supine II Study Group Prone positioning in patients with moderate and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;302(18):1977–1984. - PubMed
-
- Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard JC, Beuret P, Gacouin A, Boulain T, Mercier E, Badet M, Mercat A, Baudin O, Clavel M, Chatellier D, Jaber S, Rosselli S, Mancebo J, Sirodot M, Hilbert G, Bengler C, Richecoeur J, Gainnier M, Bayle F, Bourdin G, Leray V, Girard R, Baboi L, Ayzac L, PROSEVA Study Group Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(23):2159–2168. - PubMed
-
- Ball C, Adams J, Boyce S, Robinson P. Clinical guidelines for the use of the prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2001;17(2):94–104. - PubMed
-
- Dirkes S, Dickinson S, Havey R, O'brien D. Prone positioning: is it safe and effective? Crit Care Nurs Q. 2012;35(1):64–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

