Recent advances in bedside microcirculation assessment in critically ill patients
- PMID: 28977264
- PMCID: PMC5496759
- DOI: 10.5935/0103-507X.20170033
Recent advances in bedside microcirculation assessment in critically ill patients
Abstract
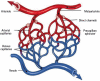
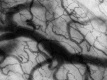
Parameters related to macrocirculation, such as the mean arterial pressure, central venous pressure, cardiac output, mixed venous saturation and central oxygen saturation, are commonly used in the hemodynamic assessment of critically ill patients. However, several studies have shown that there is a dissociation between these parameters and the state of microcirculation in this group of patients. Techniques that allow direct viewing of the microcirculation are not completely disseminated, nor are they incorporated into the clinical management of patients in shock. The numerous techniques developed for microcirculation assessment include clinical assessment (e.g., peripheral perfusion index and temperature gradient), laser Doppler flowmetry, tissue oxygen assessment electrodes, videomicroscopy (orthogonal polarization spectral imaging, sidestream dark field imaging or incident dark field illumination) and near infrared spectroscopy. In the near future, the monitoring and optimization of tissue perfusion by direct viewing and microcirculation assessment may become a goal to be achieved in the hemodynamic resuscitation of critically ill patients.
Parâmetros relacionados à macrocirculação, como pressão arterial média, pressão venosa central, débito cardíaco e saturação venosa mista e central de oxigênio, são comumente utilizados na avaliação hemodinâmica de pacientes graves. No entanto, diversos estudos demonstram que existe dissociação entre estes parâmetros e o estado da microcirculação neste grupo de pacientes. Técnicas que permitem a visualização direta da microcirculação não estão completamente difundidas e nem incorporadas ao manejo clínico dos pacientes em choque. Entre as inúmeras técnicas desenvolvidas para avaliação da microcirculação encontram-se: avaliação clínica (por exemplo: índice de perfusão periférica e gradiente de temperatura); fluxometria por laser Doppler; eletrodos de avaliação de oxigênio tecidual; videomicroscopia (imagem espectral por polarização ortogonal, análise em campo escuro de fluxo lateral, ou iluminação incidental em campo escuro); e espectroscopia no infravermelho próximo. A monitorização e a otimização da perfusão tecidual por meio da visualização direta e da avaliação da microcirculação pode, em um futuro próximo, tornar-se uma meta a ser atingida na ressuscitação hemodinâmica dos pacientes graves.
Parâmetros relacionados à macrocirculação, como pressão arterial média, pressão venosa central, débito cardíaco e saturação venosa mista e central de oxigênio, são comumente utilizados na avaliação hemodinâmica de pacientes graves. No entanto, diversos estudos demonstram que existe dissociação entre estes parâmetros e o estado da microcirculação neste grupo de pacientes. Técnicas que permitem a visualização direta da microcirculação não estão completamente difundidas e nem incorporadas ao manejo clínico dos pacientes em choque. Entre as inúmeras técnicas desenvolvidas para avaliação da microcirculação encontram-se: avaliação clínica (por exemplo: índice de perfusão periférica e gradiente de temperatura); fluxometria por laser Doppler; eletrodos de avaliação de oxigênio tecidual; videomicroscopia (imagem espectral por polarização ortogonal, análise em campo escuro de fluxo lateral, ou iluminação incidental em campo escuro); e espectroscopia no infravermelho próximo. A monitorização e a otimização da perfusão tecidual por meio da visualização direta e da avaliação da microcirculação pode, em um futuro próximo, tornar-se uma meta a ser atingida na ressuscitação hemodinâmica dos pacientes graves.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E, Tomlanovich M, Early Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative Group Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(19):1368–1377. - PubMed
-
- ARISE Investigators. ANZICS Clinical Trials Group. Peake SL, Delaney A, Bailey M, Bellomo R, Cameron PA, Cooper DJ, et al. Goal-directed resuscitation for patients with early septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(16):1496–1506. - PubMed
-
- Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power GS, Harrison DA, Sadique MZ, Grieve RD, Jahan R, Harvey SE, Bell D, Bion JF, Coats TJ, Singer M, Young JD, Rowan KM, ProMISe Trial Investigators Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(14):1301–1311. - PubMed
-
- De Backer D, Creteur J, Preiser JC, Dubois MJ, Vincent JL. Microvascular blood flow is altered in patients with sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(1):98–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

