Abasic and oxidized ribonucleotides embedded in DNA are processed by human APE1 and not by RNase H2
- PMID: 28977421
- PMCID: PMC5737539
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx723
Abasic and oxidized ribonucleotides embedded in DNA are processed by human APE1 and not by RNase H2
Abstract
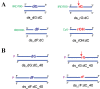
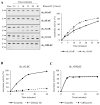
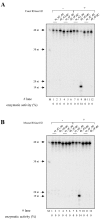
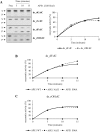
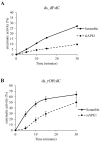
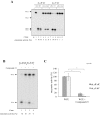
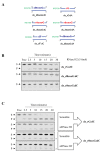
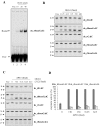
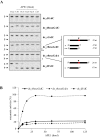
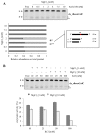
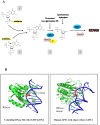
Ribonucleoside 5'-monophosphates (rNMPs) are the most common non-standard nucleotides found in DNA of eukaryotic cells, with over 100 million rNMPs transiently incorporated in the mammalian genome per cell cycle. Human ribonuclease (RNase) H2 is the principal enzyme able to cleave rNMPs in DNA. Whether RNase H2 may process abasic or oxidized rNMPs incorporated in DNA is unknown. The base excision repair (BER) pathway is mainly responsible for repairing oxidized and abasic sites into DNA. Here we show that human RNase H2 is unable to process an abasic rNMP (rAP site) or a ribose 8oxoG (r8oxoG) site embedded in DNA. On the contrary, we found that recombinant purified human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease-1 (APE1) and APE1 from human cell extracts efficiently process an rAP site in DNA and have weak endoribonuclease and 3'-exonuclease activities on r8oxoG substrate. Using biochemical assays, our results provide evidence of a human enzyme able to recognize and process abasic and oxidized ribonucleotides embedded in DNA.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Randerath K., Reddy R., Danna T.F., Watson W.P., Crane A.E., Randerath E.. Formation of ribonucleotides in DNA modified by oxidative damage in vitro and in vivo. Characterization by 32P-postlabeling. Mutat. Res. 1992; 275:355–366. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

