p53 controls expression of the DNA deaminase APOBEC3B to limit its potential mutagenic activity in cancer cells
- PMID: 28977491
- PMCID: PMC5737468
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx721
p53 controls expression of the DNA deaminase APOBEC3B to limit its potential mutagenic activity in cancer cells
Abstract
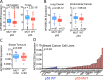
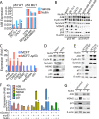
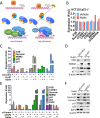
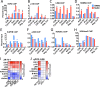
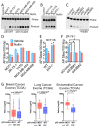
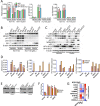
Cancer genome sequencing has implicated the cytosine deaminase activity of apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like (APOBEC) genes as an important source of mutations in diverse cancers, with APOBEC3B (A3B) expression especially correlated with such cancer mutations. To better understand the processes directing A3B over-expression in cancer, and possible therapeutic avenues for targeting A3B, we have investigated the regulation of A3B gene expression. Here, we show that A3B expression is inversely related to p53 status in different cancer types and demonstrate that this is due to a direct and pivotal role for p53 in repressing A3B expression. This occurs through the induction of p21 (CDKN1A) and the recruitment of the repressive DREAM complex to the A3B gene promoter, such that loss of p53 through mutation, or human papilloma virus-mediated inhibition, prevents recruitment of the complex, thereby causing elevated A3B expression and cytosine deaminase activity in cancer cells. As p53 is frequently mutated in cancer, our findings provide a mechanism by which p53 loss can promote cancer mutagenesis.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Chiu Y.L., Greene W.C.. The APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases: an innate defensive network opposing exogenous retroviruses and endogenous retroelements. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008; 26:317–353. - PubMed
-
- Franchini D.M., Petersen-Mahrt S.K.. AID and APOBEC deaminases: balancing DNA damage in epigenetics and immunity. Epigenomics. 2014; 6:427–443. - PubMed
-
- Ramiro A.R., Barreto V.M.. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase and active cytidine demethylation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015; 40:172–181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

