Nuclear speckles: molecular organization, biological function and role in disease
- PMID: 28977640
- PMCID: PMC5737799
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx759
Nuclear speckles: molecular organization, biological function and role in disease
Abstract
The nucleoplasm is not homogenous; it consists of many types of nuclear bodies, also known as nuclear domains or nuclear subcompartments. These self-organizing structures gather machinery involved in various nuclear activities. Nuclear speckles (NSs) or splicing speckles, also called interchromatin granule clusters, were discovered as sites for splicing factor storage and modification. Further studies on transcription and mRNA maturation and export revealed a more general role for splicing speckles in RNA metabolism. Here, we discuss the functional implications of the localization of numerous proteins crucial for epigenetic regulation, chromatin organization, DNA repair and RNA modification to nuclear speckles. We highlight recent advances suggesting that NSs facilitate integrated regulation of gene expression. In addition, we consider the influence of abundant regulatory and signaling proteins, i.e. protein kinases and proteins involved in protein ubiquitination, phosphoinositide signaling and nucleoskeletal organization, on pre-mRNA synthesis and maturation. While many of these regulatory proteins act within NSs, direct evidence for mRNA metabolism events occurring in NSs is still lacking. NSs contribute to numerous human diseases, including cancers and viral infections. In addition, recent data have demonstrated close relationships between these structures and the development of neurological disorders.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
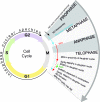
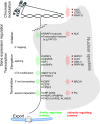
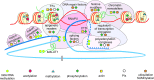

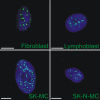
References
-
- Sahin U., Lallemand-Breitenbach V., de Thé H.. PML nuclear bodies: regulation, function and therapeutic perspectives. J. Pathol. 2014; 234:289–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

