Regulation of mitotic recombination between DNA repeats in centromeres
- PMID: 28977643
- PMCID: PMC5737691
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx763
Regulation of mitotic recombination between DNA repeats in centromeres
Erratum in
-
Regulation of mitotic recombination between DNA repeats in centromeres.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Feb 16;46(3):1562. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1310. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29346669 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
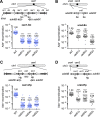
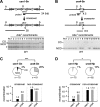
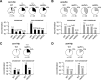
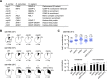
Centromeres that are essential for faithful segregation of chromosomes consist of unique DNA repeats in many eukaryotes. Although recombination is under-represented around centromeres during meiosis, little is known about recombination between centromere repeats in mitotic cells. Here, we compared spontaneous recombination that occurs between ade6B/ade6X inverted repeats integrated at centromere 1 (cen1) or at a non-centromeric ura4 locus in fission yeast. Remarkably, distinct mechanisms of homologous recombination (HR) were observed in centromere and non-centromere regions. Rad51-dependent HR that requires Rad51, Rad54 and Rad52 was predominant in the centromere, whereas Rad51-independent HR that requires Rad52 also occurred in the arm region. Crossovers between inverted repeats (i.e. inversions) were under-represented in the centromere as compared to the arm region. While heterochromatin was dispensable, Mhf1/CENP-S, Mhf2/CENP-X histone-fold proteins and Fml1/FANCM helicase were required to suppress crossovers. Furthermore, Mhf1 and Fml1 were found to prevent gross chromosomal rearrangements mediated by centromere repeats. These data for the first time uncovered the regulation of mitotic recombination between DNA repeats in centromeres and its physiological role in maintaining genome integrity.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

