De novo design and synthesis of a 30-cistron translation-factor module
- PMID: 28977654
- PMCID: PMC5737471
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx753
De novo design and synthesis of a 30-cistron translation-factor module
Abstract
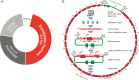
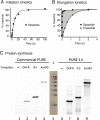
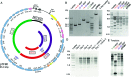
Two of the many goals of synthetic biology are synthesizing large biochemical systems and simplifying their assembly. While several genes have been assembled together by modular idempotent cloning, it is unclear if such simplified strategies scale to very large constructs for expression and purification of whole pathways. Here we synthesize from oligodeoxyribonucleotides a completely de-novo-designed, 58-kb multigene DNA. This BioBrick plasmid insert encodes 30 of the 31 translation factors of the PURE translation system, each His-tagged and in separate transcription cistrons. Dividing the insert between three high-copy expression plasmids enables the bulk purification of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and translation factors necessary for affordable, scalable reconstitution of an in vitro transcription and translation system, PURE 3.0.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Use of different tRNASer isoacceptor species in vitro to discriminate between the expression of plasmid genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1466-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1466. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982. PMID: 6803242 Free PMC article.
-
Limiting factors of the translation machinery.J Biotechnol. 2010 Oct 1;150(1):44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.07.017. Epub 2010 Jul 16. J Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20638424
-
De novo genetic codes and pure translation display.Methods. 2005 Jul;36(3):279-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2005.04.011. Methods. 2005. PMID: 16076454
-
DNA Assembly Tools and Strategies for the Generation of Plasmids.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0014-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104347 Review.
-
De novo protein synthesis in vitro.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964;3:235-97. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60743-6. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964. PMID: 5318916 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
In vitro characterisation of the MS2 RNA polymerase complex reveals host factors that modulate emesviral replicase activity.Commun Biol. 2022 Mar 25;5(1):264. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03178-2. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35338258 Free PMC article.
-
Bottom-Up Construction of Complex Biomolecular Systems With Cell-Free Synthetic Biology.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Mar 24;8:213. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00213. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32266240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programming Structured DNA Assemblies to Probe Biophysical Processes.Annu Rev Biophys. 2019 May 6;48:395-419. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-052118-115259. Annu Rev Biophys. 2019. PMID: 31084582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Free Gene Expression: Methods and Applications.Chem Rev. 2025 Jan 8;125(1):91-149. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00116. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 39700225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-free expression of RNA encoded genes using MS2 replicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Nov 18;47(20):10956-10967. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz817. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31566241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knight T. Idempotent Vector Design for Standard Assembly of Biobricks. 2003; Cambridge: MIT; http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/21168.
-
- Endy D. Foundations for engineering biology. Nature. 2005; 438:449–453. - PubMed
-
- Way J.C., Collins J.J., Keasling J.D., Silver P.A.. Integrating biological redesign: where synthetic biology came from and where it needs to go. Cell. 2014; 157:151–161. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

