Epigenetic hypomethylation and upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 28977831
- PMCID: PMC5617391
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19650
Epigenetic hypomethylation and upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in Kawasaki disease
Abstract
Background: Kawasaki disease (KD) is a type of febrile coronary vasculitis occurring in children. Some researchers have suggested that changes in genetic signatures, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), are critical markers for cardiovascular diseases. This study aims to provide a comprehensive survey of global DNA methylation levels and MMP transcripts of KD patients compared to control subjects.
Materials and methods: For chips studies, we recruited a total of 18 KD patients, prior to receiving intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and at least 3 weeks after IVIG treatment, as well as 18 healthy and 18 febrile control subjects. We applied Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip and Affymetrix GeneChip® Human Transcriptome Array 2.0 to evaluate their CpG markers and expression levels, respectively. Then we used a separate cohort to carry out real-time quantitative PCR validations of mRNA levels.
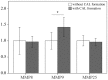
Results: The expressions of mRNA levels of MMP-8, -9, and -25 were significantly upregulated in KD patients compared to the healthy and febrile controls. Once KD patients underwent IVIG treatment, these MMPs considerably decreased. In particular, the methylation status of CpG sites of MMP-9 indicated a significant opposite tendency between both stages of not only the KD samples but also the controls. We also observed the mRNA level of MMP-9 to be higher in KD patients with coronary arterial lesion formation.
Conclusion: This study is the first to report epigenetic hypomethylation, an increased MMP-9 transcript, and the upregulation of MMP-9 in KD patients who had formed coronary arterial lesions.
Keywords: Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; Kawasaki disease; genetic methylation; matrix metalloproteinase.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All of the authors hereby declare that they have no financial interests to disclose with regard to this article.
Figures



References
-
- Kawasaki T, Kosaki F, Okawa S, Shigematsu I, Yanagawa H. A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics. 1974;54:271–6. - PubMed
-
- Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics. 2004;114:1708–33. - PubMed
-
- Hopps E, Caimi G. Matrix metalloproteases as a pharmacological target in cardiovascular diseases. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19:2583–9. - PubMed
-
- Korematsu S, Ohta Y, Tamai N, Takeguchi M, Goto C, Miyahara H, Kawano T, Izumi T. Cell distribution differences of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012;31:973–4. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31825ba6b3. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

