C-terminal kinesin motor KIFC1 participates in facilitating proper cell division of human seminoma
- PMID: 28977870
- PMCID: PMC5617430
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18139
C-terminal kinesin motor KIFC1 participates in facilitating proper cell division of human seminoma
Abstract
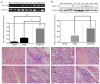
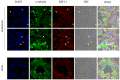
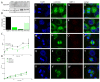
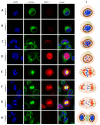
C-terminus kinesin motor KIFC1 is known for centrosome clustering in cancer cells with supernumerary centrosomes. KIFC1 crosslinks and glides on microtubules (MT) to assist normal bipolar spindle formation to avoid multi-polar cell division, which might be fatal. Testis cancer is the most common human cancer among young men. However, the gene expression profiles of testis cancer is still not complete and the expression of the C-terminus kinesin motor KIFC1 in testis cancer has not yet been examined. We found that KIFC1 is enriched in seminoma tissues in both mRNA level and protein level, and is specifically enriched in the cells that divide actively. Cell experiments showed that KIFC1 may be essential in cell division, but not essential in metastasis. Based on subcellular immuno-florescent staining results, we also described the localization of KIFC1 during cell cycle. By expressing ΔC-FLAG peptide in the cells, we found that the tail domain of KIFC1 might be essential for the dynamic disassociation of KIFC1, and the motor domain of KIFC1 might be essential for the degradation of KIFC1. Our work provides a new perspective for seminoma research.
Keywords: KIFC1; cell division; kinesin-14; seminoma; testis cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of a novel inhibitor of kinesin-like protein KIFC1.Biochem J. 2016 Apr 15;473(8):1027-35. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150992. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 26846349 Free PMC article.
-
A centrosome clustering protein, KIFC1, predicts aggressive disease course in serous ovarian adenocarcinomas.J Ovarian Res. 2016 Mar 18;9:17. doi: 10.1186/s13048-016-0224-0. J Ovarian Res. 2016. PMID: 26992853 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal kinesin motor KIFC1 may participate in nuclear reshaping and flagellum formation during spermiogenesis of Larimichthys crocea.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2017 Oct;43(5):1351-1371. doi: 10.1007/s10695-017-0377-9. Epub 2017 May 23. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28534180
-
Computational benchmarking of putative KIFC1 inhibitors.Med Res Rev. 2023 Mar;43(2):293-318. doi: 10.1002/med.21926. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Med Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36104980 Review.
-
KIFC1: a promising chemotherapy target for cancer treatment?Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48656-48670. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8799. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27102297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatics analysis to reveal key biomarkers for early and late hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Jul;9(7):4070-4079. doi: 10.21037/tcr-19-2238. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117777 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin family member C1 accelerates bladder cancer cell proliferation and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Akt/GSK3β signaling.Cancer Sci. 2019 Sep;110(9):2822-2833. doi: 10.1111/cas.14126. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31278883 Free PMC article.
-
Poly-aneuploid cancer cells promote evolvability, generating lethal cancer.Evol Appl. 2020 Feb 22;13(7):1626-1634. doi: 10.1111/eva.12929. eCollection 2020 Aug. Evol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32952609 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesins in Mammalian Spermatogenesis and Germ Cell Transport.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 25;10:837542. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.837542. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35547823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KIFC1 promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):5739-5746. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10985. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Oncol Lett. 2019. Retraction in: Oncol Lett. 2023 Jun 26;26(2):345. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13931. PMID: 31788047 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Kuwana T, Erlander M, Peterson PA, Karlsson L. Cloning and expression of HSET, a kinesin-related motor protein encoded in MHC class II region. Mol Biol Cell. 1996;7:409A. - PubMed
-
- De S, Cipriano R, Jackson MW, Stark GR. Overexpression of kinesins mediates docetaxel resistance in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:8035–42. - PubMed
-
- Rath O, Kozielski F. Kinesins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:527–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

