Correlation between estrogen receptor expression and prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 28977954
- PMCID: PMC5617514
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18253
Correlation between estrogen receptor expression and prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Accumulated studies have investigated the prognostic significance of estrogen receptor expression in epithelial ovarian cancer, but results remain controversial. The aim of this study was to perform a meta-analysis to clarify the prognostic value of estrogen receptor expression in epithelial ovarian cancer.
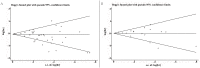
Methods: A systematic search was performed in PUBMED, EMBASE, and COCHRANE databases to identify relevant studies up to December 2016. The pooled hazard rates (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for overall survival and time to tumor progression were calculated and then weighted and pooled in this meta-analysis with a random-effect model.
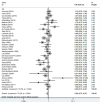
Results: Thirty-five studies with a total of 5824 patients were included. In brief, the expression of estrogen receptor was associated with an improved overall survival (HR = 0.86, 95% CI = 0.76-0.97), whereas there was no significant difference between estrogen receptor and time to tumor progression among epithelial ovarian cancer patients. Subgroup analysis revealed that estrogen receptor expression was significantly correlated with overall survival in different subgroups, such as in unclassified epithelial ovarian cancer (HR= 0.80, 95% CI = 0.66-0.95), studies using immunohistochemistry detection method (HR= 0.85, 95% CI = 0.73-1.00), European population (HR= 0.75, 95% CI = 0.60-0.94) and estrogen receptor α subtype (HR= 0.78, 95% CI = 0.62-0.98).
Conclusions: Estrogen receptor, especially estrogen receptor α, was associated with an improved overall survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Estrogen receptor expression may be a promising prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer patients.
Keywords: epithelial ovarian cancer; estrogen receptor; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Impact of estrogen receptor expression on prognosis of ovarian cancer according to antibody clone used for immunohistochemistry: a meta-analysis.J Ovarian Res. 2022 May 24;15(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-01001-4. J Ovarian Res. 2022. PMID: 35610648 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of estrogen receptor-β expression on breast cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Feb;156(1):149-62. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3721-3. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26902609
-
Prognostic Value of Circulating Tumor Cells in Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 22;10(6):e0130873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130873. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26098665 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of progesterone receptor expression in ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(22):36845-36856. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15982. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic value of the miR-200 family in ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2016 May;95(5):505-12. doi: 10.1111/aogs.12883. Epub 2016 Mar 27. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2016. PMID: 26910180 Review.
Cited by
-
CA-125:CA72-4 ratio - towards a promising cost-effective tool in ovarian cancer diagnosis and monitoring of post-menopausal women under hormone treatment.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Aug 10;17(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01487-0. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 39127704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased risk of ovarian cancer associated with rs9898876 sex hormone-binding globulin gene variant.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):4537-4544. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07297-1. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35277784
-
The Role of the Estrogen Pathway in the Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 19;19(2):611. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020611. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29463044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hormone replacement therapy after surgery for epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 28;1(1):CD012559. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012559.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31989588 Free PMC article.
-
Linking obesity-induced leptin-signaling pathways to common endocrine-related cancers in women.Endocrine. 2019 Jan;63(1):3-17. doi: 10.1007/s12020-018-1748-4. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Endocrine. 2019. PMID: 30218381 Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Tkalia IG, Vorobyova LI, Svintsitsky VS, Nespryadko SV, Goncharuk IV, Lukyanova NY, Chekhun VF. Clinical significance of hormonal receptor status of malignant ovarian tumors. Exp Oncol. 2014;36:125–133. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

