Genomic alterations in mucins across cancers
- PMID: 28978023
- PMCID: PMC5620163
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17934
Genomic alterations in mucins across cancers
Abstract
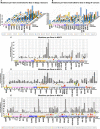
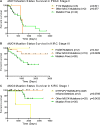
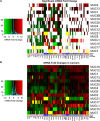
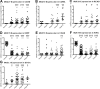
The significance of mucins in cancers has led to the development of novel biomarkers and therapeutic agents against cancers. Despite significant advances in the understanding of mucins, systemic investigations into the role of mucins in cancer biology focusing particularly on the histological subtypes and stages, along with other variables, are yet to be carried out to discover potential novel functions and cancer-specific roles. Here, we investigated 11 mucin expressing cancers for DNA mutations, mRNA expression, copy number, methylation, and the impacts these genomic features may have on patient survival by utilizing The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset. We demonstrate that mucin DNA mutations have a significant rate, pattern, and impact on cancer patient survival depending on the tissue of origin. This includes a frequent T112P mutation in MUC1 that is seen in half of the pancreatic MUC1 mutations, as well as being present in other cancers. We also observed a very frequent MUC4 mutation at H4205, which correlated with survival outcomes in patients. Furthermore, we observed significant alterations in mucin mRNA expression in multiple tumor types. Our results demonstrate de novo expression of certain mucins in cancer tissues, including MUC21 in colorectal cancers. We observed a general decrease in promoter methylation for mucins, which correlated with decreased expression of many genes, such as MUC15 in kidney cancers. Lastly, several mucin gene loci demonstrated copy number increase in multiple histological subtypes. Thus, our study presents a comprehensive analysis of genomic alterations in mucins and their corresponding roles in cancer progression.
Keywords: MUC1; cancer genetic profiles; cancer genetics; genetic alterations; mucins.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts interests exist.
Figures

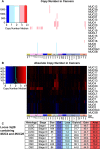
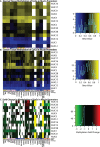
References
-
- Bottoni P, Scatena R. The role of CA 125 as tumor marker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;867:229–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-7215-0_14 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrianifahanana M, Moniaux N, Batra SK. Regulation of mucin expression: mechanistic aspects and implications for cancer and inflammatory diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1765:189–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.01.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bafna S, Kaur S, Batra SK. Membrane-bound mucins: the mechanistic basis for alterations in the growth and survival of cancer cells. Oncogene. 2010;29:2893–904. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.87 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tang H, Singh S, Partyka K, Kletter D, Hsueh P, Yadav J, Ensink E, Bern M, Hostetter G, Hartman D, Huang Y, Brand RE, Haab BB. Glycan motif profiling reveals plasma sialyl-lewis x elevations in pancreatic cancers that are negative for sialyl-lewis A. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015;14:1323–33. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M114.047837 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

