Therapeutic efficacy of SYM004, a mixture of two anti-EGFR antibodies in human colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to cetuximab and MET activation
- PMID: 28978055
- PMCID: PMC5620195
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18749
Therapeutic efficacy of SYM004, a mixture of two anti-EGFR antibodies in human colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to cetuximab and MET activation
Abstract
Purpose: Cetuximab and panitumumab have an effective therapeutic response in a subset of RAS Wild-Type (WT) metastatic colorectal cancers (mCRCs). Despite molecular-driven selection, all patients do not respond to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors and the onset of secondary resistance limits their clinical benefit.
Experimental design: We tested, in vitro and in vivo, the effect of SYM004, a 1:1 mixture of two recombinant human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against non-overlapping epitopes of the EGFR, on CRC models with acquired resistance to cetuximab.
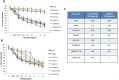
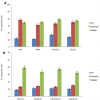
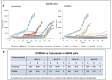
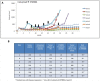
Results: SYM004 showed a potent growth inhibitory effect in CRC cell lines with acquired resistance to cetuximab and MET activation. SYM004 treatment determined a significant induction of apoptosis and a strong inhibition of MET, AKT and MAPK phosphorilation in these resistant models. The data may further suggest SYM004 -driven induced internalization and degradation of the antibody-receptor complex, which prevents cross-interaction between EGFR and MET even in the presence of TGFα. Moreover, in vivo xenograft studies demonstrated that SYM004 has stronger antitumor activity than cetuximab in CRC models. Importantly, in the current work we observed a response to therapy in all cetuximab resistant tumors mice treated with SYM004. More importantly, four out of seven mice continue to respond to SYM004 after 30 weeks of treatment underling the prolonged effect of the drug.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the treatment with SYM004 could be a strategy to overcome acquired resistance to first generation of anti-EGFR therapies in mCRC as a result of MET activation.
Keywords: MET; SYM004; acquired resistance; cetuximab; metastatic colorectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Dr. Napolitano and all coauthors have no conflicts of interest to declare for the following manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21254 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello F, Tortora G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1160–74. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0707704 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Troiani T, Napolitano S, Della Corte CM, Martini G, Martinelli E, Morgillo F, Ciardiello F. Therapeutic value of EGFR inhibition in CRC and NSCLC: 15 years of clinical evidence. ESMO Open. 2016;1:e000088. https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2016-000088 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:341–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1609 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A, D’Haens G, Pintér T, Lim R, Bodoky G, Roh JK, Folprecht G, Ruff P, et al. Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1408–17. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0805019 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

