miR-30e* is overexpressed in prostate cancer and promotes NF-κB-mediated proliferation and tumor growth
- PMID: 28978058
- PMCID: PMC5620198
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18795
miR-30e* is overexpressed in prostate cancer and promotes NF-κB-mediated proliferation and tumor growth
Abstract
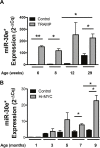
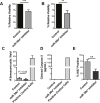
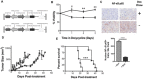
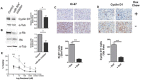
According to the CDC prostate cancer (CaP) has the highest incidence and second highest mortality rate amongst cancers in American men. Constitutive NF-κB activation is a hallmark of CaP and this pathway drives many pro-tumorigenic characteristics of CaP cells, including cell proliferation and survival. An activated NF-κB gene signature is predictive of CaP progression and biochemical recurrence following therapeutic intervention. However, the mechanisms that perpetuate NF-κB activation are incompletely understood. Genes that control NF-κB activity are rarely mutated in CaP suggesting that epigenetic mechanisms may contribute to constitutive NF-κB activation. microRNAs (miRs) epigenetically regulate many genes involved with NF-κB activation. IκBα is a direct inhibitor of NF-κB; it binds to and sequesters NF-κB in the cytoplasm resulting in functional inhibition. IκBα is a target gene of miR-30e* yet the expression and oncological impact of miR-30e* in CaP is unknown. We report that miR-30e* expression is elevated in multiple murine models of CaP and is most pronounced in late stage disease. miR-30e* drives CaP proliferation and tumor growth through inhibition of IκBα, which results in chronic activation of NF-κB. Additionally, we show that inhibition of miR-30e* improves chemotherapeutic control of CaP. Thus, miR-30e* may prove to be a novel clinical target whose inhibition leads to decreased CaP cell proliferation and sensitization of CaP cells to chemotherapeutics.
Keywords: NF-κB; cyclin D1; microRNA; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-30e* promotes human glioma cell invasiveness in an orthotopic xenotransplantation model by disrupting the NF-κB/IκBα negative feedback loop.J Clin Invest. 2012 Jan;122(1):33-47. doi: 10.1172/JCI58849. Epub 2011 Dec 12. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22156201 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-30e* suppresses dengue virus replication by promoting NF-κB-dependent IFN production.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Aug 14;8(8):e3088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003088. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 25122182 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of microRNA-30e-producing recombinant viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) and its effect on in vitro immune responses.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Nov;94:381-388. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.09.026. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31521783
-
Upregulation of MicroRNA 711 Mediates HIV-1 Vpr Promotion of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency and Induction of Pro-proliferation and Pro-survival Cytokines by Targeting the Notch/NF-κB-Signaling Axis.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00580-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00580-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29976660 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB activation in human prostate cancer: important mediator or epiphenomenon?J Cell Biochem. 2004 Jan 1;91(1):100-17. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10729. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 14689584 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-6852 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion via targeting forkhead box J1 in gastric cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3249-3255. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6569. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30214548 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of maximal androgen blockade and radical prostatectomy on urinary extracellular vesicle miRNA expression.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 28;42(6):185. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02730-4. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40293608
-
MicroRNA-30e inhibits adhesion, migration, invasion and cell cycle progression of prostate cancer cells via inhibition of the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway by downregulating CHRM3.Int J Oncol. 2019 Feb;54(2):443-454. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4647. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Int J Oncol. 2019. Retraction in: Int J Oncol. 2024 Sep;65(3):82. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5670. PMID: 30483762 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Cross Talk between MicroRNAs and Dengue Virus.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024 Apr 2;110(5):856-867. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0546. Print 2024 May 1. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024. PMID: 38579704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Roles in the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway in Cancer.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 19;9:546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00546. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

