Immunotherapy of WAP-TNP mice with early stage mammary gland tumors
- PMID: 28978072
- PMCID: PMC5620212
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18850
Immunotherapy of WAP-TNP mice with early stage mammary gland tumors
Abstract
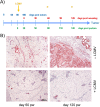
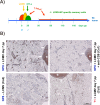
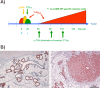
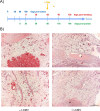
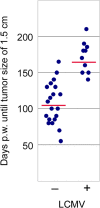
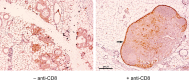
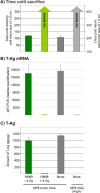
The SV40 transgenic BALB/c mouse based WAP-T/WAP-TNP model for triple-negative breast cancer allows the analysis of parameters influencing immunotherapeutic approaches. Except for WAP-TNP tumors expressing the immune-dominant LCMV NP-epitope within SV40 T-antigen (T-AgNP) which is not expressed by T-Ag of WAP-T tumors, the tumors are extremely similar. Comparative anti-PD1/PD-L1 immunotherapy of WAP-T and WAP-TNP mice supported the hypothesis that the immunogenicity of tumor antigen T-cell epitopes strongly influences the success of immune checkpoint blockade therapy, with highly immunogenic T-cell epitopes favoring rapid CTL exhaustion. Here we analyzed the immune response in NP8 mice during early times of tumor development. LCMV infection of lactating NP8 mice induced lifelong tumor protection by memory CTLs. Immunization with LCMV after involution and appearance of T-AgNP expressing parity-induced tumor progenitor cells could not cure the mice, as memory CTLs became exhausted. However, immunization significantly prolonged the time of tumor outgrowth. Elimination of exhausted CTLs and of immunosuppressive cells by sub-lethal γ-irradiation, followed by adoptive transfer of NP-epitope specific CTLs into NP8 tumor mice with early lesions, completely prevented tumor outgrowth, when lymphocytes obtained after injection of weakly immunogenic NP8 tumor-derived cells into BALB/c mice were transferred. Transfer of lymphocytes obtained after infection of BALB/c mice with highly immunogenic LCMV into such mice delayed tumor outgrowth for a significant period, but could not prevent it. We conclude that eliminating exhausted CTLs and immune-suppressive cells followed by transfer or generation of low-avidity tumor antigen-specific CTLs might be a promising approach for curative tumor immunotherapy.
Keywords: CTL exhaustion; LCMV NP T-cell epitope; SV40 T-antigen; adoptive transfer of low/high avidity CTLs; transgenic breast cancer mouse model.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T-cell epitope strength in WAP-T mouse mammary carcinomas is an important determinant in PD1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):64543-64559. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11620. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27579535 Free PMC article.
-
An inducible transgenic mouse breast cancer model for the analysis of tumor antigen specific CD8+ T-cell responses.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 17;6(36):38487-503. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5750. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26513294 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity is a decisive feature for the metastatic outgrowth of disseminated WAP-T mouse mammary carcinoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2015 Mar 26;15:178. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1165-5. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25886487 Free PMC article.
-
SV40 T/t-antigen induces premature mammary gland involution by apoptosis and selects for p53 missense mutation in mammary tumors.Oncogene. 1998 Apr 23;16(16):2103-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201733. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9572491
-
SV40 T-antigen induces breast cancer formation with a high efficiency in lactating and virgin WAP-SV-T transgenic animals but with a low efficiency in ovariectomized animals.Oncogene. 1996 Feb 1;12(3):495-505. Oncogene. 1996. PMID: 8637705
References
-
- Jannasch K, Dullin C, Heinlein C, Krepulat F, Wegwitz F, Deppert W, Alves F. Detection of different tumor growth kinetics in single transgenic mice with oncogene-induced mammary carcinomas by flat-panel volume computed tomography. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:62–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

