Low-dose photon irradiation induces invasiveness through the SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway in malignant mesothelioma cells
- PMID: 28978091
- PMCID: PMC5620231
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19134
Low-dose photon irradiation induces invasiveness through the SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway in malignant mesothelioma cells
Abstract
Background: Low-dose photon irradiation has repeatedly been suspected to increase a risk of promoting local recurrence of disease or even systemic dissemination. The purpose of this study was to investigate the motility of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) cell lines after low-doses of photon irradiation and to elucidate the mechanism of the detected phenotype.
Methods: H28 and H226 MPM cells were examined in clonogenic survival experiments and migration assays with and without various doses of photon and carbon ion irradiation. C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), SDF-1α, β1 integrin, α3 integrin, and α5 integrin expressions were analyzed by quantitative FACS analysis, ELISA and western blots. Apoptosis was assessed via Annexin-V-staining.
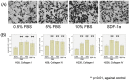
Results: The migration of MPM cells was stimulated by both fetal bovine serum and by stromal cell-derived factor 1α (SDF-1α). Low doses of photon irradiation (1 Gy and 2 Gy) suppressed clonogenicity, but promoted migration of both H28 and H226 cells through the SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway. Hypermigration was inhibited by the administration of CXCR4 antagonist, AMD3100. In contrast, corresponding doses of carbon ion irradiation (0.3 Gy and 1 Gy) suppressed clonogenicity, but did not promote MPM cell migration.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that the co-administration of photon irradiation and the CXCR4-antagonist AMD3100 or the use of carbon ions instead of photons may be possible solutions to reduce the risk of locoregional tumor recurrence after radiotherapy for MPM.
Keywords: CXCR4; SDF-1α; carbon ion irradiation; mesothelioma; photon irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No conflict declared.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 enhanced motility of human osteosarcoma cells involves MEK1/2, ERK and NF-kappaB-dependent pathways.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Oct;221(1):204-12. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21846. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19496172
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 enhances motility and integrin up-regulation through CXCR4, ERK and NF-kappaB-dependent pathway in human lung cancer cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Dec 15;74(12):1702-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.08.025. Epub 2007 Aug 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17904532
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediates radiation-induced invasiveness through the SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2015 May 10;6(13):10893-907. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3535. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25843954 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of integrin α5β1 inhibition on SDF-l/CXCR4-mediated choroidal neovascularization.Int J Ophthalmol. 2018 May 18;11(5):726-735. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.05.04. eCollection 2018. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29862169 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal-derived factor-1alpha/CXCL12-CXCR 4 axis is involved in the dissemination of NSCLC cells into pleural space.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004 May;30(5):671-7. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0340OC. Epub 2003 Dec 12. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004. Retraction in: Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Sep;39(3):380. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.39.3.380. PMID: 14672915 Retracted.
Cited by
-
Potential Role of CXCR4 Targeting in the Context of Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy of Cancer.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 21;9:3018. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03018. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30622535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mozobil® (Plerixafor, AMD3100), 10 years after its approval by the US Food and Drug Administration.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2019 Jan-Dec;27:2040206619829382. doi: 10.1177/2040206619829382. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30776910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-induced alterations in immunogenicity of a murine pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell line.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 20;10(1):686. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57456-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31959787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singhal S, Kaiser LR. Malignant mesothelioma: options for management. Surg Clin North Am. 2002;82:797–831. - PubMed
-
- Treasure T, Utley M. Ten traps for the unwary in surgical series: a case study in mesothelioma reports. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133:1414–8. - PubMed
-
- Rea F, Marulli G, Bortolotti L, Breda C, Favaretto AG, Loreggian L, Sartori F. Induction chemotherapy, extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP) and adjuvant hemi-thoracic radiation in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM): feasibility and results. Lung Cancer. 2007;57:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Flores RM, Krug LM, Rosenzweig KE, Venkatraman E, Vincent A, Heelan R, Akhurst T, Rusch VW. Induction chemotherapy, extrapleural pneumonectomy, and postoperative high-dose radiotherapy for locally advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma: a phase II trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2006;1:289–95. - PubMed
-
- Krug LM, Pass HI, Rusch VW, Kindler HL, Sugarbaker DJ, Rosenzweig KE, Flores R, Friedberg JS, Pisters K, Monberg M, Obasaju CK, Vogelzang NJ. Multicenter phase II trial of neoadjuvant pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy and radiation for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3007–13. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

