High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin and the Risk Stratification of Patients With Renal Impairment Presenting With Suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome
- PMID: 28978551
- PMCID: PMC5793996
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030320
High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin and the Risk Stratification of Patients With Renal Impairment Presenting With Suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome
Abstract
Background: High-sensitivity cardiac troponin testing may improve the risk stratification and diagnosis of myocardial infarction, but concentrations can be challenging to interpret in patients with renal impairment, and the effectiveness of testing in this group is uncertain.
Methods: In a prospective multicenter study of consecutive patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome, we evaluated the performance of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I in those with and without renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate <60mL/min/1.73m2). The negative predictive value and sensitivity of troponin concentrations below the risk stratification threshold (5 ng/L) at presentation were reported for a primary outcome of index type 1 myocardial infarction, or type 1 myocardial infarction or cardiac death at 30 days. The positive predictive value and specificity at the 99th centile diagnostic threshold (16 ng/L in women, 34 ng/L in men) was determined for index type 1 myocardial infarction. Subsequent type 1 myocardial infarction and cardiac death were reported at 1 year.
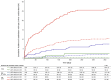
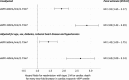
Results: Of 4726 patients identified, 904 (19%) had renal impairment. Troponin concentrations <5 ng/L at presentation identified 17% of patients with renal impairment as low risk for the primary outcome (negative predictive value, 98.4%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 96.0%-99.7%; sensitivity 98.9%; 95%CI, 97.5%-99.9%), in comparison with 56% without renal impairment (P<0.001) with similar performance (negative predictive value, 99.7%; 95% CI, 99.4%-99.9%; sensitivity 98.4%; 95% CI, 97.2%-99.4%). The positive predictive value and specificity at the 99th centile were lower in patients with renal impairment at 50.0% (95% CI, 45.2%-54.8%) and 70.9% (95% CI, 67.5%-74.2%), respectively, in comparison with 62.4% (95% CI, 58.8%-65.9%) and 92.1% (95% CI, 91.2%-93.0%) in those without. At 1 year, patients with troponin concentrations >99th centile and renal impairment were at greater risk of subsequent myocardial infarction or cardiac death than those with normal renal function (24% versus 10%; adjusted hazard ratio, 2.19; 95% CI, 1.54-3.11).
Conclusions: In suspected acute coronary syndrome, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin identified fewer patients with renal impairment as low risk and more as high risk, but with lower specificity for type 1 myocardial infarction. Irrespective of diagnosis, patients with renal impairment and elevated cardiac troponin concentrations had a 2-fold greater risk of a major cardiac event than those with normal renal function, and should be considered for further investigation and treatment.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01852123.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; myocardial infarction; renal insufficiency; risk; troponin.
© 2017 The Authors.
Figures

Comment in
-
The Cardiac Troponin Renal Disease Diagnostic Conundrum: Past, Present, and Future.Circulation. 2018 Jan 30;137(5):452-454. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031717. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29378755 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gansevoort RT, Correa-Rotter R, Hemmelgarn BR, Jafar TH, Heerspink HJ, Mann JF, Matsushita K, Wen CP. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet. 2013;382:339–352. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60595-4. - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, Gansevoort RT Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;375:2073–2081. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60674-5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van der Velde M, Matsushita K, Coresh J, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey A, de Jong P, Gansevoort RT, van der Velde M, Matsushita K, Coresh J, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Gansevoort RT, Levey A, El-Nahas M, Eckardt KU, Kasiske BL, Ninomiya T, Chalmers J, Macmahon S, Tonelli M, Hemmelgarn B, Sacks F, Curhan G, Collins AJ, Li S, Chen SC, Hawaii Cohort KP, Lee BJ, Ishani A, Neaton J, Svendsen K, Mann JF, Yusuf S, Teo KK, Gao P, Nelson RG, Knowler WC, Bilo HJ, Joosten H, Kleefstra N, Groenier KH, Auguste P, Veldhuis K, Wang Y, Camarata L, Thomas B, Manley T Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. A collaborative meta-analysis of high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011;79:1341–1352. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.536. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Muntner P, Chen AY, Alexander KP, Roe MT, Cannon CP, Saucedo JF, Kontos MC, Wiviott SD Acute Coronary Treatment and Intervention Outcomes Network registry. Use of evidence-based therapies in short-term outcomes of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in patients with chronic kidney disease: a report from the National Cardiovascular Data Acute Coronary Treatment and Intervention Outcomes Network registry. Circulation. 2010;121:357–365. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.865352. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anavekar NS, McMurray JJ, Velazquez EJ, Solomon SD, Kober L, Rouleau JL, White HD, Nordlander R, Maggioni A, Dickstein K, Zelenkofske S, Leimberger JD, Califf RM, Pfeffer MA. Relation between renal dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1285–1295. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa041365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

