HIV-related Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia managed with caspofungin and veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation rescue therapy
- PMID: 28978595
- PMCID: PMC5652506
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221214
HIV-related Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia managed with caspofungin and veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation rescue therapy
Abstract
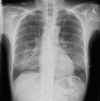
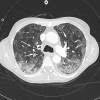
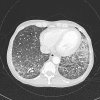
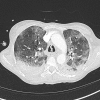
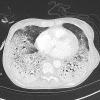
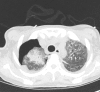
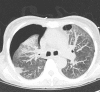
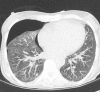
Patients with pneumocystis pneumonia have a risk of progressing to acute respiratory failure necessitating admission to intensive care. The case described is of a patient with a newly diagnosed HIV infection presenting with pneumocystis pneumonia. Despite initiating the appropriate pharmacological treatment the patient's clinical condition deteriorated, and required both rescue pharmacological therapy with echinocandins as well as respiratory support with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy. The patient recovered well on ventilator and circulatory support despite a long weaning process complicated by sequelae common to pneumocystis pneumonia. Following initialisation of antiretroviral therapy and step-down from an intensive care setting, the patient required further prolonged hospital stay for rehabilitation and mental health support before being discharged. This case reviews the novel pharmacological therapies and respiratory support strategies used in cases of pneumocystis pneumonia, including the clinical and psychological sequelae that may follow.
Keywords: HIV/AIDS; adult intensive care; mechanical ventilation.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a 29-Year-Old Man with Pneumocystis jirovecii Respiratory Failure and AIDS.Tex Heart Inst J. 2018 Aug 1;45(4):254-259. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-16-6186. eCollection 2018 Aug. Tex Heart Inst J. 2018. PMID: 30374241 Free PMC article.
-
Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in an Immunocompromised Patient without HIV Infection.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2020 Apr;250(4):215-221. doi: 10.1620/tjem.250.215. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32249237
-
Extra corporeal membrane oxygenation to facilitate lung protective ventilation and prevent ventilator-induced lung injury in severe Pneumocystis pneumonia with pneumomediastinum: a case report and short literature review.BMC Pulm Med. 2016 Apr 14;16(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12890-016-0214-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2016. PMID: 27080997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VV-ECMO combined with prone position ventilation in the treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jan 7;101(1):e28482. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028482. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35029898 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, Diagnostic, and Treatment Disparities between HIV-Infected and Non-HIV-Infected Immunocompromised Patients with Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia.Respiration. 2018;96(1):52-65. doi: 10.1159/000487713. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Respiration. 2018. PMID: 29635251 Review.
Cited by
-
Caspofungin and Pneumocystis Pneumonia: It Is Time To Go Ahead.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 23;63(10):e01296-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01296-19. Print 2019 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31548210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in immunocompromised patients with acute respiratory failure: A retrospective cohort study.Clin Respir J. 2023 Sep;17(9):874-883. doi: 10.1111/crj.13674. Epub 2023 Aug 27. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37634899 Free PMC article.
-
A Pilot Study of Echinocandin Combination with Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole and Clindamycin for the Treatment of AIDS Patients with Pneumocystis Pneumonia.J Immunol Res. 2019 Dec 1;2019:8105075. doi: 10.1155/2019/8105075. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31886310 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a 29-Year-Old Man with Pneumocystis jirovecii Respiratory Failure and AIDS.Tex Heart Inst J. 2018 Aug 1;45(4):254-259. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-16-6186. eCollection 2018 Aug. Tex Heart Inst J. 2018. PMID: 30374241 Free PMC article.
-
Favourable outcome after prolonged veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-V ECMO) support for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in a renal transplant recipient.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Apr 1;14(4):e240004. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-240004. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33795271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galloway R, Guerra M, Shadomy S. Control of Communicable Diseases Manual : Heymann DL, Washington D.C: American Public Health Association, 2015:348–53.
-
- Calderón EJ, Gutiérrez-Rivero S, Durand-Joly I, et al. . Pneumocystis infection in humans: diagnosis and treatment. ExpertRevAntiInfectTher 2010;8:683–701. - PubMed
-
- Bozzette SA, Sattler FR, Chiu J, et al. . A controlled trial of early adjunctive treatment with corticosteroids for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. California Collaborative Treatment Group. N Engl J Med 1990;323:1451–7. 10.1056/NEJM199011223232104 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
