Neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies prevent Zika virus infection in macaques
- PMID: 28978754
- PMCID: PMC6155977
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aan8184
Neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies prevent Zika virus infection in macaques
Abstract
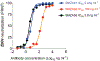
Therapies to prevent maternal Zika virus (ZIKV) infection and its subsequent fetal developmental complications are urgently required. We isolated three potent ZIKV-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (nmAbs) from the plasmablasts of a ZIKV-infected patient-SMZAb1, SMZAb2, and SMZAb5-directed against two different domains of the virus. We engineered these nmAbs with Fc LALA mutations that abrogate Fcγ receptor binding, thus eliminating potential therapy-mediated antibody-dependent enhancement. We administered a cocktail of these three nmAbs to nonhuman primates 1 day before challenge with ZIKV and demonstrated that the nmAbs completely prevented viremia in serum after challenge. Given that numerous antibodies have exceptional safety profiles in humans, the cocktail described here could be rapidly developed to protect uninfected pregnant women and their fetuses.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures


References
-
- Brasil P, Pereira JP Jr., Moreira ME, Ribeiro Nogueira RM, Damasceno L, Wakimoto M, Rabello RS, Valderramos SG, Halai UA, Salles TS, Zin AA, Horovitz D, Daltro P, Boechat M, Raja Gabaglia C, Carvalho de Sequeira P, Pilotto JH, Medialdea-Carrera R, Cotrim da Cunha D, Abreu de Carvalho LM, Pone M, Machado Siqueira A, Calvet GA, Rodrigues Baiao AE, Neves ES, Nassar de Carvalho PR, Hasue RH, Marschik PB, Einspieler C, Janzen C, Cherry JD, Bispo de Filippis AM, Nielsen-Saines K, Zika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women in Rio de Janeiro. The New England journal of medicine 375, 2321–2334 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mlakar J, Korva M, Tul N, Popovic M, Poljsak-Prijatelj M, Mraz J, Kolenc M, Resman Rus K, Vesnaver Vipotnik T, Fabjan Vodusek V, Vizjak A, Pizem J, Petrovec M, Avsic Zupanc T, Zika Virus Associated with Microcephaly. The New England journal of medicine 374, 951–958 (2016). - PubMed
-
- WHO, Fifth meeting of the Emergency Committee under the International Health Regulations (2005) regarding microcephaly, other neurological disorders and Zika virus. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/statements/2016/zika-fifth-ec/en/. (Accessed on Aug 24, 2017).
-
- The IMpact-RSV Study Group, Palivizumab, a humanized respiratory syncytial virus monoclonal antibody, reduces hospitalization from respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants. The IMpact-RSV Study Group. Pediatrics 102, 531–537 (1998). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

