Enzyme-based amperometric galactose biosensors: a review
- PMID: 28979051
- PMCID: PMC5597680
- DOI: 10.1007/s00604-017-2465-z
Enzyme-based amperometric galactose biosensors: a review
Abstract
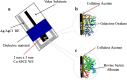
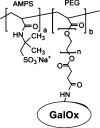
This review (with 35 references) summarizes the various strategies used in biosensors for galactose, and their analytical performance. A brief comparison of the enzyme immobilization methods employed and the analytical performance characteristics of a range of galactose biosensors are first summarized in tabular form and then described in detail. Selected examples have been included to demonstrate the various applications of these biosensors to real samples. Following an introduction into the field that covers the significance of sensing galactose in various fields, the review covers biosensors based on the use of galactose oxidase, with a discussion of methods for their immobilization (via cross-linking, adsorption, covalent bonding and entrapment). This is followed by a short section on biosensors based on the use of galactose dehydrogenase. The conclusion section summarizes the state of the art and addresses current challenges. Graphical abstractFabrication of a disposable screen-printed (a) electrochemical galactose biosensor (b) for real sample analysis and a dummy biosensor
Keywords: Disposable sensors; Electrochemistry; Enzyme immobilization; Galactose dehydrogenase; Galactose oxidase; Glucose; Hydrogen peroxide; Modified electrodes; Redox mediators; Screen-printed electrodes.
(c) for compensating the effect of interferences.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Tkáč J, Gemeiner P, Šturdik E. Rapid and sensitive galactose oxidase-peroxidase biosensor for galactose detection with prolonged stability. Biotechnol Tech. 1999;13:931–936. doi: 10.1023/A:1008966413722. - DOI
-
- Kanyong P, Pemberton RM, Jackson SK, Hart JP. Amperometric screen-printed galactose biosensor for cell toxicity applications. Anal Lett. 2016;49:236–244. doi: 10.1080/00032719.2015.1070166. - DOI
-
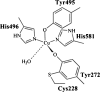
- Baron AJ, Stevens C, Wilmot C, Seneviratnes KD, Blakeley V, Dooley DM, Phillips SEV, Knowles PF, McPherson MJ. Structure and mechanism of galactose oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:250095–225105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
