Comparison of intraocular pressure fluctuations before and after ab interno trabeculectomy in pseudoexfoliation glaucoma patients
- PMID: 28979095
- PMCID: PMC5606685
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S143061
Comparison of intraocular pressure fluctuations before and after ab interno trabeculectomy in pseudoexfoliation glaucoma patients
Abstract
Purpose: Ab interno trabeculectomy (AIT) with the Trabectome has been shown to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) in eyes with pseudoexfoliation (PEX) glaucoma. Here, we examined the change of IOP fluctuations before and after only AIT or AIT with cataract surgery in PEX patients using the contact lens sensor Triggerfish®.
Methods: This was a prospective open-label study. Twenty-four consecutive patients with PEX glaucoma were included. Twelve patients underwent cataract surgery and AIT (triple-surgery group), and 12 patients underwent only AIT (single-surgery group). In each eye, IOP fluctuations over 24 h were measured with the contact lens sensor before and at 3 months after the surgery. We compared the change of IOP fluctuation before and after operation. We also evaluated the difference in IOP changes between the triple- and single-surgery groups.
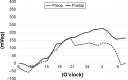
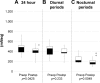
Results: At 3 months after the surgeries, the mean IOP was significantly reduced from 23.5±6.5 mmHg to 14.6±2.8 mmHg in the single-surgery group and from 22.5±3.0 mmHg to 11.5±2.9 mmHg in the triple-surgery group. The mean IOP reduction rate was significantly higher in the triple-surgery group compared to the single-surgery group (p=0.0358). In both groups, the mean range of IOP fluctuations was significantly decreased during nocturnal periods. The mean range of 24 h IOP fluctuations was decreased in the triple-surgery group (p=0.00425), not in the single-surgery group (p=0.970).
Conclusion: Triple surgery could decrease IOP value and the IOP fluctuations to a greater extent than single surgery in PEX glaucoma patients.
Keywords: ab interno trabeculectomy; contact lens sensor; fluctuation; intraocular pressure; pseudoexfoliation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Ritch R, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U. Exfoliation syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 2001;45(4):265–315. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P, Wang JJ, Hourihan F, Healey PR, Mitchell P. The relationship between glaucoma and pseudoexfoliation: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999;117(10):1319–1324. - PubMed
-
- Ritch R, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U. Exfoliation (pseudoexfoliation) syndrome: toward a new understanding. Proceedings of the First International Think Tank. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2001;79(2):213–217. - PubMed
-
- Teus MA, Castejon MA, Calvo MA, Pérez-Salaíces P, Marcos A. Intraocular pressure as a risk factor for visual field loss in pseudoexfoliative and in primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1998;105(12):2225–2229. - PubMed
-
- Grodum K, Heijl A, Bengtsson B. Risk of glaucoma in ocular hypertension with and without pseudoexfoliation. Ophthalmology. 2005;112(3):386–390. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

