Dupilumab in the management of moderate-to-severe asthma: the data so far
- PMID: 28979129
- PMCID: PMC5589101
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S125964
Dupilumab in the management of moderate-to-severe asthma: the data so far
Abstract
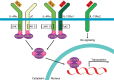
Severe asthma constitutes illness in a relatively small proportion of all patients with asthma, but it is a major public health problem - with considerable effect on morbidity, mortality, as well as a high burden on health care resources. Regardless of effective treatments being widely available and the existence of treatment guidelines, a large population of severe asthma cases remain uncontrolled. Achieving and maintaining asthma control in this group of patients is, therefore, of utmost importance. The recognition of distinct inflammatory phenotypes within this population has driven the development of targeted biological therapies - particularly, selective targeted monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). It is noteworthy that in approximately 50% of these patients, there is strong evidence of the pathogenic role of T helper type-2 (Th2) cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13, orchestrating the eosinophilic and allergic inflammatory processes. Among the recently developed antiasthma biologic drugs, the mAb dupilumab is very promising given its ability to inhibit the biological effects of both IL-4 and IL-13. In this review, we focused on IL-4 and IL-13, as these interleukins are considered to play a key role in the pathophysiology of asthma, and on dupilumab, an anti-IL-4 receptor human mAb, as a forthcoming treatment for uncontrolled severe asthma in the near future.
Keywords: asthma; dupilumab; interleukin-13; interleukin-4; monoclonal antibodies; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. GINA. [homepage on the Internet] [Accessed June 7, 2017]. Available from: www.ginasthma.org.
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur Respir J. 2014;43(2):343–373. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan PW, Campbell JD, Ghushchyan VH, Globe G. Outcomes before and after treatment after escalation to Global Initiative for Asthma steps 4 and 5 in severe asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015;114(6):462–469. - PubMed
-
- Accordini S, Corsico AG, Braggion M, et al. The cost of persistent asthma in Europe: an international population-based study in adults. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;160(1):93–101. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

