The role of smartphones in encouraging physical activity in adults
- PMID: 28979157
- PMCID: PMC5602432
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S134095
The role of smartphones in encouraging physical activity in adults
Abstract
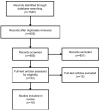
Lack of physical activity is a global public health issue. Behavioral change interventions utilizing smartphone applications (apps) are considered a potential solution. The purpose of this literature review was to: 1) determine whether smartphone-based interventions encourage the initiation of, and participation in, physical activity; 2) explore the success of interventions in different populations; and 3) examine the key factors of the interventions that successfully encouraged physical activity. Eight databases (Medline, Scopus, EBM Reviews-Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, EBM Reviews-Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, PsycInfo, SportDISCUS, CINAHL, and EMBASE) were searched and studies reporting physical activity outcomes following interventions using smartphone apps in adults were included in the narrative review. Results were mixed with eight studies reporting increased physical activity and ten reporting no change. Interventions did not appear to be successful in specific populations defined by age, sex, country, or clinical diagnosis. There was no conclusive evidence that a specific behavioral theory or behavioral change technique was superior in eliciting behavioral change. The literature remains limited primarily to short-term studies, many of which are underpowered feasibility or pilot studies; therefore, many knowledge gaps regarding the effectiveness of smartphone apps in encouraging physical activity remain. Robust studies that can accommodate the fast pace of the technology industry are needed to examine outcomes in large populations.
Keywords: behavioral change; exercise; mobile health; public health.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Comment in
-
In response to The role of smartphones in encouraging physical activity in adults.Int J Gen Med. 2017 Dec 1;10:451-454. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S151758. eCollection 2017. Int J Gen Med. 2017. PMID: 29271980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks. Geneva: Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2009.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health. Geneva: Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2010. - PubMed
-
- Colley RC, Garriguet D, Janssen I, Craig CL, Clarke J, Tremblay MS. Physical activity of Canadian adults: accelerometer results from the 2007 to 2009 Canadian Health Measures Survey. Health Rep. 2011;22(1):7–14. - PubMed
-
- Tucker JM, Welk GJ, Beyler NK. Physical activity in U.S.: adults compliance with the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40(4):454–461. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources