Protective Effect of a Polyherbal Traditional Formula Consisting of Rosa damascena Mill., Glycyrrhiza glabra L. And Nardostachys jatamansi DC., Against Ethanol-induced Gastric Ulcer
- PMID: 28979324
- PMCID: PMC5603879
Protective Effect of a Polyherbal Traditional Formula Consisting of Rosa damascena Mill., Glycyrrhiza glabra L. And Nardostachys jatamansi DC., Against Ethanol-induced Gastric Ulcer
Abstract
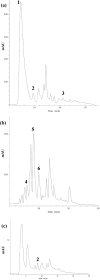
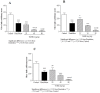
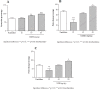
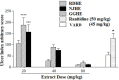
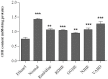
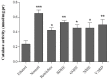
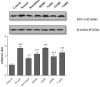
"VARD" formula consisting of Rosa damascena Mill. (Rosaceae) petals, and rhizomes of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. (Papilionaceae) and Nardostachys jatamansi DC. (Valerianaceae), has been proposed for gastric ulcer in Iranian traditional medicine. We investigated the antiulcer activity of each plant separately and in combination. The biochemical and molecular functions of extracts were also evaluated. Each plant hydroalcoholic extract was standardized via determination of total phenolic and flavonoid contents, also via some phenolic compounds determination and specially glycyrrhizic acid in G. glabra by using HPLC. Rats received orally extracts of the plants (20, 40 and 80 mg/Kg) and "VARD" (45 mg/Kg) 1 h before ethanol administration. Two h after receiving ethanol, animals were sacrificed; the stomach was removed for macroscopic and microscopic assessment. Also heme-oxygenase-1, glutathione, and catalase were measured in the gastric tissue of the rats pretreated by "VARD" and dose of 20 mg/Kg of extracts. Among three extracts, R. damascena and G. glabra contained more total phenolic and flavonoid content respectively. Gallic acid was prominent compound in R. damascena. The extracts of R. damascena, G. glabra, and N. jatamansi significantly decreased ulcer index. ED50 values were 8.2, 31.86 and 25.08 mg/Kg respectively. "VARD" significantly decreased ulcer index compared to 20 mg/Kg of G. glabra (p < 0.0001) and N. jatamansi (p < 0.001). Pretreatment with "VARD" and each plant extracts (20 mg/Kg) increased glutathione, catalse and heme-oxygenase-1 significantly (p < 0.05) in comparison with control group. Our findings indicate that "VARD" partly via antioxidant activity can be considered as an effective antiulcer formula.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Glycyrrhiza glabra; Heme-oxygenase-1; Inflammation; Nardostachys jatamansi; Peptic ulcer; Rosa damascena.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Majumdar D, Atherton J. Peptic ulcers and their complications. Surgery. . 2006;24:110–4.
-
- Sung JJY, Kuipers EJ, Elserag HB. Systematic review: the global incidence and prevalence of peptic ulcer disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. . 2009;29:938–46. - PubMed
-
- Fauci A, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, et al. Peptic Ulcer Disease and Related Disorders In: Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 17th ed. New York : McGraw-Hill; 2008.
-
- Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. Sleisenger and Fordtran›s gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 9th ed. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders; 2010. chapter 52.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
