Oily Skin: A review of Treatment Options
- PMID: 28979664
- PMCID: PMC5605215
Oily Skin: A review of Treatment Options
Abstract
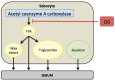
One of the most common dermatologic concerns is oily skin, and the demand for effective treatment options is ever apparent. This review article addresses numerous topical treatment options such as retinoids, olumacostat glasaretil, and various cosmeceutical agents. several systemic and procedural techniques that incorporate isotretinoin, spironolactone, oral contraceptives, botulinum toxin, photodynamic therapy, and lasers are reviewed as well. Each treatment option is analyzed in terms of the proposed mechanism of action, efficacy reported in the literature, and potential adverse effects.
Keywords: L-carnitine; Oily skin; botulinum toxin; diode laser; green tea; isotretinoin; niacinamide; olumacostat glasaretil; oral contraceptives; photodynamic therapy; seborrhea; sebum production; spironolactone; topical retinoids.
Conflict of interest statement
FUNDING:No funding was provided for this article. DISCLOSURES:The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- schaller M, Plewig G. Structure and function of eccrine, apocrine, and sebaceous glands. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizza JL, schaffer JV, editors. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2012. 539 pp.544 pp.
-
- Leyden JJ. New understandings of the pathogenesis of acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:s15–25. - PubMed
-
- Nikkari T. Comparative chemistryofsebum. J Invest Dermatol. 1974;62:257–267. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources