Lumen apposing metal stents for pancreatic fluid collections: Recognition and management of complications
- PMID: 28979710
- PMCID: PMC5605345
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i9.456
Lumen apposing metal stents for pancreatic fluid collections: Recognition and management of complications
Abstract
For patients recovering from acute pancreatitis, the development of a pancreatic fluid collection (PFC) predicts a more complex course of recovery, and introduces difficult management decisions with regard to when, whether, and how the collection should be drained. Most PFCs resolve spontaneously and drainage is indicated only in pseudocysts and walled-off pancreatic necrosis when the collections are causing symptoms and/or local complications such as biliary obstruction. Historical approaches to PFC drainage have included surgical (open or laparoscopic cystgastrostomy or pancreatic debridement), and the placement of percutaneous drains. Endoscopic drainage techniques have emerged in the last several years as the preferred approach for most patients, when local expertise is available. Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) have recently been developed as a tool to facilitate potentially safer and easier endoscopic drainage of pancreatic fluid collections, and less commonly, for other indications, such as gallbladder drainage. Physicians considering LAMS placement must be aware of the complications most commonly associated with LAMS including bleeding, migration, buried stent, stent occlusion, and perforation. Because of the patient complexity associated with severe pancreatitis, management of pancreatic fluid collections can be a complex and multidisciplinary endeavor. Successful and safe use of LAMS for patients with pancreatic fluid collections requires that the endoscopist have a full understanding of the potential complications of LAMS techniques, including how to recognize and manage expected complications.
Keywords: Cystgastrostomy; Endoscopic necrosectomy; Lumen apposing metal stent; Pancreatic fluid collection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Dr. Berzin is a consultant and speaker for Boston Scientific.
Figures
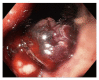
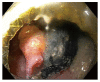
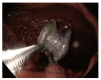
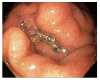
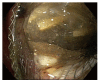
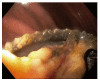
References
-
- Forsmark ChE, Vege SS, Wilcox CM. Acute Pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:598–599. - PubMed
-
- Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG, Vege SS; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Sutton BS, Trevino JM, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Equal efficacy of endoscopic and surgical cystogastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage in a randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:583–590.e1. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

