Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells derived Muscle Progenitors Effectively Mitigate Muscular Dystrophy through Restoring the Dystrophin Distribution
- PMID: 28979820
- PMCID: PMC5624556
- DOI: 10.4172/2157-7633.1000361
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells derived Muscle Progenitors Effectively Mitigate Muscular Dystrophy through Restoring the Dystrophin Distribution
Abstract
Background: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a recessive form of muscular disorder, resulting from the dystrophin gene mutations in X-chromosome. Application of embryonic stem cells or adult stem cells has demonstrated the therapeutic effects on DMD through both cell-based and non-cell based mechanisms. In this study, we proposed that Myogenic Progenitor Cells from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSC-MPCs) would be more effective in repairing muscle damage caused by muscular dystrophy.
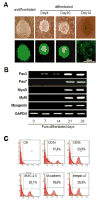
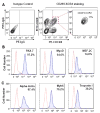
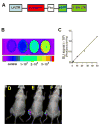
Methods and results: Mouse iPSCs were cultured in myogenic differentiation culture medium and the MPCs were characterized using Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and flow cytometry. iPSCs were successfully converted into MPCs, as evidenced by the distinct expression of myogenic genes and cell surface markers. The muscle injury was induced in tibialis muscle of mdx mouse by cardiotoxin injection, and the iPSC-MPCs were then engrafted into the damage site. Firefly luciferase expression vector was transduced into iPSC-MPCs and the in vivo bioluminescence imaging analysis revealed that these progenitor cells survived even at 30-days post transplantation. Importantly, histological analysis revealed that the central nuclei percentage, as well as fibrosis, was significantly reduced in the iPSC-MPCs treated muscle. In addition,the transplantation of progenitor cells restored the distributions of dystrophin and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors together with up-regulation of pair box protein 7(Pax7), a myogenic transcription factor.
Conclusion: iPSCs-derived MPCs exert strong therapeutic effects on muscular dystrophy by restoring dystrophin expression and acetylcholine receptor distribution.
Keywords: Duchenne muscular dystrophy; Dystrophin; Muscular progenitors; iPSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Statement The authors confirmed that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Peter AK, Miller G, Crosbie RH. Disrupted mechanical stability of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex causes severe muscular dystrophy in sarcospan transgenic mice. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:996–1008. - PubMed
-
- Pestronk A, Parhad IM, Drachman DB, Price DL. Membrane myopathy: morphological similarities to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1982;5:209–214. - PubMed
-
- Zhou M, Feng YP, Zhang C. Gold clusters on Nb-doped SrTiO3: effects of metal-insulator transition on heterogeneous Au nanocatalysis. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2012;14:9660–9665. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
