The periplasmic binding protein NrtT affects xantham gum production and pathogenesis in Xanthomonas citri
- PMID: 28979839
- PMCID: PMC5623697
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12281
The periplasmic binding protein NrtT affects xantham gum production and pathogenesis in Xanthomonas citri
Abstract
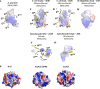
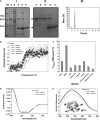
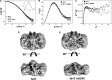
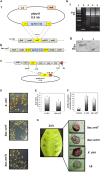
In Xanthomonas citri, the bacterium that causes citrus canker, three ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are known to be dedicated to the uptake of sulfur compounds. In this work, using functional, biophysical and structural methods, we showed that NrtT, a periplasmic component of the ABC transporter NrtCB, is an alkanesulfonate-binding protein and that the deletion of the nrtT gene affected xantham gum synthesis, adhesion and biofilm production, similarly to the phenotype obtained in the X. citri ssuA-knockout strain, in which the alkanesulfonate-binding protein SsuA is absent. Although NrtA and SsuA share similar ligands, the function of these proteins is not complementary. These results emphasize that organic-sulfur sources are directly involved with bacterial infection in vivo and are needed for pathogenesis in X. citri.
Keywords: ABC transporter; NrtT; Xanthomonas citri; alkanesulfonates/taurine; pathogenesis; periplasmic binding protein.
Figures



References
-
- da Silva ACR, Ferro JA, Reinach FC, Farah CS, Furlan LR, Quaggio RB, Monteiro‐Vitorello CB, Van Sluys MA, Almeida NF, Alves LM et al (2002) Comparison of the genomes of two Xanthomonas pathogens with differing host specificities. Nature 414, 459–463. - PubMed
-
- Gottwald TR, Graham JH and Schubert TS (2002) Citrus canker: the pathogen and its impact. Plant Health Prog 10, 1–34.
-
- Civerolo E (1984) Bacterial canker disease of citrus. J Rio Gd Val Hortic Soc 37, 127–146.
-
- Brunings A and Gabriel D (2003) Xanthomonas citri: breaking the surface. Mol Plant Pathol 4, 141–157. - PubMed
-
- Graham JH, Gottwald TR, Cubero J and Achor AD (2004) Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri: factors affecting successful eradication of citrus canker. Mol Plant Pathol 5, 1–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

