Pedunculopontine glutamatergic neurons control spike patterning in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 28980939
- PMCID: PMC5643088
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.30352
Pedunculopontine glutamatergic neurons control spike patterning in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
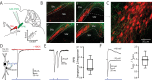
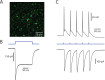
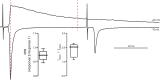
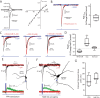
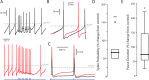
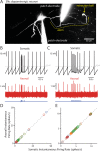
Burst spiking in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) dopaminergic neurons is a key signaling event in the circuitry controlling goal-directed behavior. It is widely believed that this spiking mode depends upon an interaction between synaptic activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and intrinsic oscillatory mechanisms. However, the role of specific neural networks in burst generation has not been defined. To begin filling this gap, SNc glutamatergic synapses arising from pedunculopotine nucleus (PPN) neurons were characterized using optical and electrophysiological approaches. These synapses were localized exclusively on the soma and proximal dendrites, placing them in a good location to influence spike generation. Indeed, optogenetic stimulation of PPN axons reliably evoked spiking in SNc dopaminergic neurons. Moreover, burst stimulation of PPN axons was faithfully followed, even in the presence of NMDAR antagonists. Thus, PPN-evoked burst spiking of SNc dopaminergic neurons in vivo may not only be extrinsically triggered, but extrinsically patterned as well.
Keywords: basal ganglia; burst firing; dopamine; glutamate; mouse; neuroscience; pedunculopontine nucleus.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures
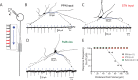

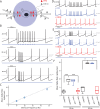
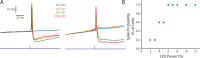
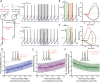
References
-
- Alderson HL, Latimer MP, Winn P. A functional dissociation of the anterior and posterior pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: excitotoxic lesions have differential effects on locomotion and the response to nicotine. Brain Structure and Function. 2008;213:247–253. doi: 10.1007/s00429-008-0174-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bortolanza M, Wietzikoski EC, Boschen SL, Dombrowski PA, Latimer M, Maclaren DA, Winn P, Da Cunha C. Functional disconnection of the substantia nigra pars compacta from the pedunculopontine nucleus impairs learning of a conditioned avoidance task. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 2010;94:229–239. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.05.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

