A role for LAX2 in regulating xylem development and lateral-vein symmetry in the leaf
- PMID: 28981582
- PMCID: PMC5737667
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcx091
A role for LAX2 in regulating xylem development and lateral-vein symmetry in the leaf
Abstract
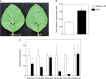
Background and aims: The symmetry of venation patterning in leaves is highly conserved within a plant species. Auxins are involved in this process and also in xylem vasculature development. Studying transgenic Arabidopsis plants ectopically expressing the sunflower transcription factor HaHB4, it was observed that there was a significant lateral-vein asymmetry in leaves and in xylem formation compared to wild type plants. To unravel the molecular mechanisms behind this phenotype, genes differentially expressed in these plants and related to auxin influx were investigated.
Methods: Candidate genes responsible for the observed phenotypes were selected using a co-expression analysis. Single and multiple mutants in auxin influx carriers were characterized by morphological, physiological and molecular techniques. The analysis was further complemented by restoring the wild type (WT) phenotype by mutant complementation studies and using transgenic soybean plants ectopically expressing HaHB4 .
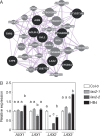
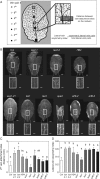
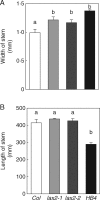
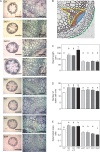
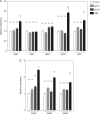
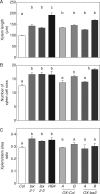
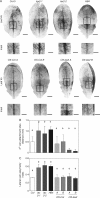
Key results: LAX2 , down-regulated in HaHB4 transgenic plants, was bioinformatically chosen as a candidate gene. The quadruple mutant aux1 lax1 lax2 lax3 and the single mutants, except lax1, presented an enhanced asymmetry in venation patterning. Additionally, the xylem vasculature of the lax2 mutant and the HaHB4 -expressing plants differed from the WT vasculature, including increased xylem length and number of xylem cell rows. Complementation of the lax2 mutant with the LAX2 gene restored both lateral-vein symmetry and xylem/stem area ratio in the stem, showing that auxin homeostasis is required to achieve normal vascular development. Interestingly, soybean plants ectopically expressing HaHB4 also showed an increased asymmetry in the venation patterning, accompanied by the repression of several GmLAX genes.
Conclusions: Auxin influx carriers have a significant role in leaf venation pattering in leaves and, in particular, LAX2 is required for normal xylem development, probablt controlling auxin homeostasis.
Keywords: Auxin influx carriers; HD-Zip I; HaHB4; LAX2; vascular patterning; venation symmetry; xylem organization.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Annals of Botany Company. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures
References
-
- Aloni R. 2001. Foliar and axial aspects of vascular differentiation: hypotheses and evidence. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 20: 22–34.
-
- Aloni R. 2010. The induction of vascular tissues by auxin In: Davies PJ, ed. Plant hormones: biosynthesis, signal transduction, action! Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 485–518.
-
- Aloni R, Schwalm K, Langhans M, Ullrich CI.. 2003. Gradual shifts in sites of free-auxin production during leaf-primordium development and their role in vascular differentiation and leaf morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Planta 216: 841–853. - PubMed
-
- Arcadia-Biosciences. 2015. Verdeca’s HB4 stress tolerance trait completes US Food and Drug Administration early food safety evaluation. http://www.arcadiabio.com/news/press-release/verdeca%E2%80%99s-hb4-stres...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

