Effect of Adalimumab on Clinical Outcomes and Health-related Quality of Life Among Patients With Ulcerative Colitis in a Clinical Practice Setting: Results From InspirADA
- PMID: 28981846
- PMCID: PMC5881702
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx093
Effect of Adalimumab on Clinical Outcomes and Health-related Quality of Life Among Patients With Ulcerative Colitis in a Clinical Practice Setting: Results From InspirADA
Abstract
Background and aims: Randomised trials have described the benefits of adalimumab [ADA] for ulcerative colitis [UC]; however, few data are available on health-related quality of life [HRQL] and health care costs in clinical practice.
Methods: InspirADA, a multicentre, prospective study, evaluated the effect of ADA in patients with moderate to severe UC treated according to usual clinical practice. Outcomes assessed were: Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index [SCCAI] response/remission rates; changes in HRQL; all-cause direct costs; and UC-related direct and indirect costs from baseline to Week 26.
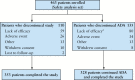
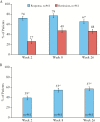
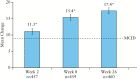
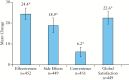
Results: Data from 463 patients were analysed. At Week 26, 67% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 62%, 71%) of patients achieved response; 48% [95% CI: 44%, 53%] were in remission. For the overall population, significant [all p < 0.001] improvements from baseline to Week 26 were observed for the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire [SIBDQ] (mean change ± standard deviation [SD]: 17.4 ± 14.5) and the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions-5 Level [EQ-5D-5L] (index: 0.1 ± 0.2; visual analogue scale [VAS]: 19.5 ± 25.8). Parallel improvements were seen in work productivity [11% absolute decrease in absenteeism; 25% absolute decrease in impairment while working; and 27% absolute decrease in impairment of ability to perform daily activities, all p < 0.001]. Among study completers, cumulative all-cause medical costs and UC-related medical costs were significantly [both p < 0.001] reduced by 59% and 77%, respectively, 6 months after initiation of therapy compared with the preceding 6 months. The safety profile of ADA was consistent with that observed in previous clinical trials.
Conclusions: ADA therapy in usual clinical practice is effective at improving and maintaining symptomatic control, improving HRQL, and decreasing costs of medical care among patients with UC.
Keywords: Ulcerative colitis; health care costs; patient outcomes.
© European Crohn’s and Colitis Organistion (ECCO) 2017.
Figures

References
-
- Danese S, Fiocchi C. Ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 2011;365:1713–25. - PubMed
-
- Dignass A, Eliakim R, Magro F et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 1: definitions and diagnosis. J Crohns Colitis 2012;6:965–90. - PubMed
-
- Dignass A, Lindsay JO, Sturm A et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis 2012;6:991–1030. - PubMed
-
- Van Assche G, Dignass A, Bokemeyer B et al. ; European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 3: special situations. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:1–33. - PubMed
-
- Janke KH, Raible A, Bauer M et al. Questions on life satisfaction [FLZM] in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 2004;19:343–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

