Psoralea corylifolia extract induces vasodilation in rat arteries through both endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms involving inhibition of TRPC3 channel activity and elaboration of prostaglandin
- PMID: 28982307
- PMCID: PMC6130690
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1383484
Psoralea corylifolia extract induces vasodilation in rat arteries through both endothelium-dependent and -independent mechanisms involving inhibition of TRPC3 channel activity and elaboration of prostaglandin
Abstract
Context: Fructus Psoralea, Psoralea corylifolia L. (Leguminosae), has been widely used in traditional medicines for the treatment of dermatitis, leukoderma, asthma and osteoporosis.
Objectives: In this study, we sought to study mechanisms underlying the vasoactive properties of Psoralea corylifolia extract (PCE) and its active ingredients.
Materials and methods: To study mechanisms underlying the vasoactive properties of PCE prepared by extracting dried seeds of Psoralea corylifolia with 70% ethanol, isometric tension recordings of rat aortic rings and the ionic currents through TRPC3 (transient receptor potential canonical 3) channels were measured with the cumulative concentration (10-600 μg/mL) of PCE or its constituents.
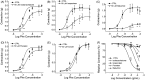
Results: Cumulative treatment with PCE caused the relaxation of pre-contracted aortic rings in the presence and absence of endothelium with EC50 values of 61.27 ± 3.11 and 211.13 ± 18.74 μg/mL, respectively. Pretreatment with inhibitors of nitric oxide (NO) synthase, guanylate cyclase, or cyclooxygenase and pyrazole 3, a selective TRPC3 channel blocker, significantly decreased PCE-induced vasorelaxation (p < 0.01). The PCE constituents, bakuchiol, isobavachalcone, isopsoralen and psoralen, inhibited hTRPC3 currents (inhibited by 40.6 ± 2.7, 27.1 ± 7.9, 35.1 ± 4.8 and 47.4 ± 3.9%, respectively). Furthermore, these constituents significantly relaxed pre-contracted aortic rings (EC50 128.9, 4.5, 32.1 and 114.9 μg/mL, respectively).
Discussion and conclusions: Taken together, our data indicate that the vasodilatory actions of PCE are dependent on endothelial NO/cGMP and also involved in prostaglandin production. PCE and its active constituents, bakuchiol, isobavachalcone, isopsoralen and psoralen, caused dose-dependent inhibition of TRPC3 channels, indicating that those ingredients attenuate Phe-induced vasoconstriction.
Keywords: COX; Ethanol extract; hypotensive; nitric oxide; non-selective cation channel.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Vasorelaxant effects of Cerebralcare Granule® are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, potassium channel opening and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):572-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.062. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24924524
-
A UPLC-MS/MS method for in vivo and in vitro pharmacokinetic studies of psoralenoside, isopsoralenoside, psoralen and isopsoralen from Psoralea corylifolia extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):609-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.11.013. Epub 2013 Dec 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24315982
-
The mechanism of vasorelaxation induced by ethanol extract of Sophora flavescens in rat aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):547-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.06.013. Epub 2011 Jun 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21704693
-
Bakuchiol: A Potential Anticancer Compound from Psoralea corylifolia Linn.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023;23(9):989-998. doi: 10.2174/1871520623666230130102910. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36717993 Review.
-
Therapeutic and Health Promoting Potential of Bakuchiol from Psoralea corylifolia: A Comprehensive Review.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023;23(9):1125-1136. doi: 10.2174/1871530323666230207123613. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 36748816 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects and Mechanisms of Five Psoralea Prenylflavonoids on Aging-Related Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 17;2020:2128513. doi: 10.1155/2020/2128513. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32655760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Exposure of Psoralen and Isopsoralen Induced Hepatotoxicity and Serum Metabolites Profiles Changes in Female Rats.Metabolites. 2019 Nov 2;9(11):263. doi: 10.3390/metabo9110263. Metabolites. 2019. PMID: 31684074 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Activities of Psoralidin: A Comprehensive Review of the Molecular Mechanisms of Action.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 22;11:571459. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.571459. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33192514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of Psoralea corylifolia L.: a valuable plant with profound biological significance.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 20;15:1521040. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1521040. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39902075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasorelaxant effects of biochemical constituents of various medicinal plants and their benefits in diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):1122-1141. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1122. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38983824 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bapat K, Chintalwar GJ, Pandey U, Thakur VS, Sarma HD, Samuel G, Pillai MR, Chattopadhyay S, Venkatesh M.. 2005. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of radioiodinated bakuchiol as an anti-tumor agent. Appl Radiat Isot. 62:389–393. - PubMed
-
- Baranowska M, Kozlowska H, Korbut A, Malinowska B.. 2007. Potassium channels in blood vessels: their role in health and disease. Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 61:596–605. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri RK, Bojanowski K.. 2014. Bakuchiol: a retinol-like functional compound revealed by gene expression profiling and clinically proven to have anti-aging effects. Int J Cosmet Sci. 36:221–230. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
