Use of a channelized Hotelling observer to assess CT image quality and optimize dose reduction for iteratively reconstructed images
- PMID: 28983493
- PMCID: PMC5624940
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.3.031213
Use of a channelized Hotelling observer to assess CT image quality and optimize dose reduction for iteratively reconstructed images
Abstract
The use of iterative reconstruction (IR) algorithms in CT generally decreases image noise and enables dose reduction. However, the amount of dose reduction possible using IR without sacrificing diagnostic performance is difficult to assess with conventional image quality metrics. Through this investigation, achievable dose reduction using a commercially available IR algorithm without loss of low contrast spatial resolution was determined with a channelized Hotelling observer (CHO) model and used to optimize a clinical abdomen/pelvis exam protocol. A phantom containing 21 low contrast disks-three different contrast levels and seven different diameters-was imaged at different dose levels. Images were created with filtered backprojection (FBP) and IR. The CHO was tasked with detecting the low contrast disks. CHO performance indicated dose could be reduced by 22% to 25% without compromising low contrast detectability (as compared to full-dose FBP images) whereas 50% or more dose reduction significantly reduced detection performance. Importantly, default settings for the scanner and protocol investigated reduced dose by upward of 75%. Subsequently, CHO-based protocol changes to the default protocol yielded images of higher quality and doses more consistent with values from a larger, dose-optimized scanner fleet. CHO assessment provided objective data to successfully optimize a clinical CT acquisition protocol.
Keywords: channelized Hotelling observer; computed tomography; iterative reconstruction; low contrast resolution; radiation dose.
Figures

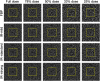

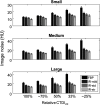


References
-
- Angel E., “AIDR 3D iterative reconstruction: integrated, automated and adaptive dose reduction,” Tustin, California: (2012).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

