Circular RNA expression profiles and features in human tissues: a study using RNA-seq data
- PMID: 28984197
- PMCID: PMC5629547
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-4029-3
Circular RNA expression profiles and features in human tissues: a study using RNA-seq data
Abstract
Background: Circular RNA (circRNA) is one type of noncoding RNA that forms a covalently closed continuous loop. Similar to long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), circRNA can act as microRNA (miRNA) 'sponges' to regulate gene expression, and its abnormal expression is related to diseases such as atherosclerosis, nervous system disorders and cancer. So far, there have been no systematic studies on circRNA abundance and expression profiles in human adult and fetal tissues.
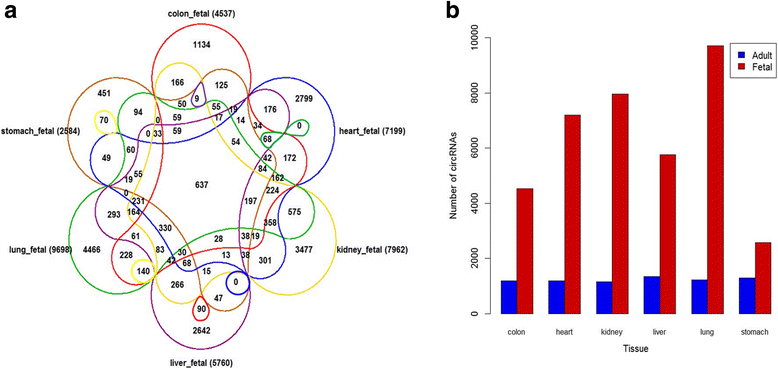
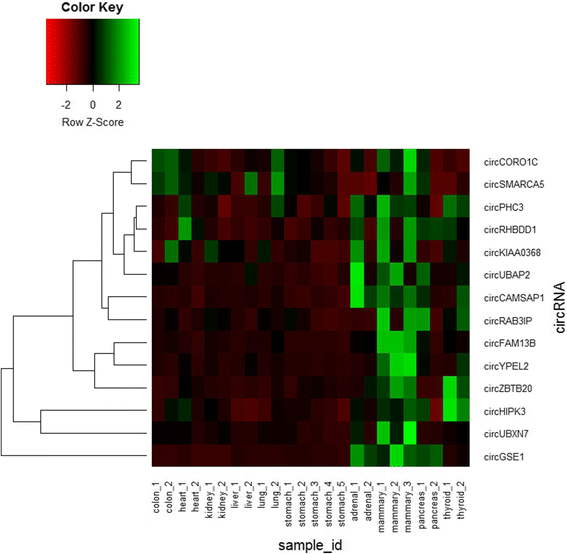
Results: We explored circRNA expression profiles using RNA-seq data for six adult and fetal normal tissues (colon, heart, kidney, liver, lung, and stomach) and four gland normal tissues (adrenal gland, mammary gland, pancreas, and thyroid gland). A total of 8120, 25,933 and 14,433 circRNAs were detected by at least two supporting junction reads in adult, fetal and gland tissues, respectively. Among them, 3092, 14,241 and 6879 circRNAs were novel when compared to the published results. In each adult tissue type, we found at least 1000 circRNAs, among which 36.97-50.04% were tissue-specific. We reported 33 circRNAs that were ubiquitously expressed in all the adult tissues we examined. To further explore the potential "housekeeping" function of these circRNAs, we constructed a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network containing 17 circRNAs, 22 miRNAs and 90 mRNAs. Furthermore, we found that both the abundance and the relative expression level of circRNAs were higher in fetal tissue than adult tissue. The number of circRNAs in gland tissues, especially in mammary gland (9665 circRNA candidates), was higher than that of other adult tissues (1160-3777).
Conclusions: We systematically investigated circRNA expression in a variety of human adult and fetal tissues. Our observation of different expression level of circRNAs in adult and fetal tissues suggested that circRNAs might play their role in a tissue-specific and development-specific fashion. Analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network provided potential targets of circRNAs. High expression level of circRNAs in mammary gland might be attributed to the rich innervation.
Keywords: Circular RNA; Expression profile; Mammary gland; Regulatory network; Tissue specificity; microRNA ‘sponge’.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

