New perspectives for targeting RAF kinase in human cancer
- PMID: 28984291
- PMCID: PMC6000833
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc.2017.79
New perspectives for targeting RAF kinase in human cancer
Abstract
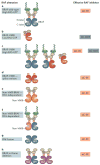
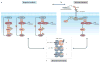
The discovery that a subset of human tumours is dependent on mutationally deregulated BRAF kinase intensified the development of RAF inhibitors to be used as potential therapeutics. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved second-generation RAF inhibitors vemurafenib and dabrafenib have elicited remarkable responses and improved survival of patients with BRAF-V600E/K melanoma, but their effectiveness is limited by resistance. Beyond melanoma, current clinical RAF inhibitors show modest efficacy when used for colorectal and thyroid BRAF-V600E tumours or for tumours harbouring BRAF alterations other than the V600 mutation. Accumulated experimental and clinical evidence indicates that the complex biochemical mechanisms of RAF kinase signalling account both for the effectiveness of RAF inhibitors and for the various mechanisms of tumour resistance to them. Recently, a number of next-generation RAF inhibitors, with diverse structural and biochemical properties, have entered preclinical and clinical development. In this Review, we discuss the current understanding of RAF kinase regulation, mechanisms of inhibitor action and related clinical resistance to these drugs. The recent elucidation of critical structural and biochemical aspects of RAF inhibitor action, combined with the availability of a number of structurally diverse RAF inhibitors currently in preclinical and clinical development, will enable the design of more effective RAF inhibitors and RAF-inhibitor-based therapeutic strategies, tailored to different clinical contexts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lavoie H, Therrien M. Regulation of RAF protein kinases in ERK signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:281–298. - PubMed
-
- Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3279–3290. - PubMed
-
- Wellbrock C, Karasarides M, Marais R. The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:875–885. - PubMed
-
- Roberts PJ, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3291–3310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

