Expression Profiling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Genes Reveals Their Evolutionary and Functional Diversity in Different Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis) Cultivars
- PMID: 28984837
- PMCID: PMC5664111
- DOI: 10.3390/genes8100261
Expression Profiling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Genes Reveals Their Evolutionary and Functional Diversity in Different Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis) Cultivars
Abstract
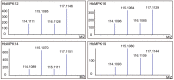
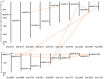
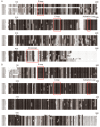
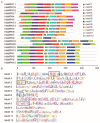
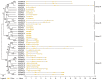
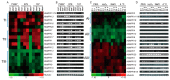
Rubber tree (Heveabrasiliensis) is the only commercially cultivated plant for producing natural rubber, one of the most essential industrial raw materials. Knowledge of the evolutionary and functional characteristics of kinases in H. brasiliensis is limited because of the long growth period and lack of well annotated genome information. Here, we reported mitogen-activated protein kinases in H.brasiliensis (HbMPKs) by manually checking and correcting the rubber tree genome. Of the 20 identified HbMPKs, four members were validated by proteomic data. Protein motif and phylogenetic analyses classified these members into four known groups comprising Thr-Glu-Tyr (TEY) and Thr-Asp-Tyr (TDY) domains, respectively. Evolutionary and syntenic analyses suggested four duplication events: HbMPK3/HbMPK6, HbMPK8/HbMPK9/HbMPK15, HbMPK10/HbMPK12 and HbMPK11/HbMPK16/HbMPK19. Expression profiling of the identified HbMPKs in roots, stems, leaves and latex obtained from three cultivars with different latex yield ability revealed tissue- and variety-expression specificity of HbMPK paralogues. Gene expression patterns under osmotic, oxidative, salt and cold stresses, combined with cis-element distribution analyses, indicated different regulation patterns of HbMPK paralogues. Further, Ka/Ks and Tajima analyses suggested an accelerated evolutionary rate in paralogues HbMPK10/12. These results revealed HbMPKs have diverse functions in natural rubber biosynthesis, and highlighted the potential possibility of using MPKs to improve stress tolerance in future rubber tree breeding.
Keywords: Hevea brasiliensis; abiotic stress; functional diversity; gene family evolution; mitogen-activated protein kinase; natural rubber biosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yamashita S., Yamaguchi H., Waki T., Aoki Y., Mizuno M., Yanbe F., Ishii T., Funaki A., Tozawa Y., Miyagi-Inoue Y., et al. Identification and reconstitution of the rubber biosynthetic machinery on rubber particles from Hevea brasiliensis. eLife. 2016;5:19022. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

