Chronic disease research in Europe and the need for integrated population cohorts
- PMID: 28986739
- PMCID: PMC5662668
- DOI: 10.1007/s10654-017-0315-2
Chronic disease research in Europe and the need for integrated population cohorts
Conflict of interest statement
Institutional grants from the European Union funded a small part of Professor Gert-Jan van Ommen’s salary through Leiden University Medical Center.
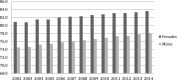
Figures

Comment in
-
To see and then to act, that is the challenge.Eur J Epidemiol. 2017 Sep;32(9):737-739. doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0317-0. Epub 2017 Oct 7. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28988343 No abstract available.
References
-
- Eurostat Statistics Explained. Mortality and life expectancy statistics. http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Mortality_an... (2016). Accessed on 21 Dec 2016.
-
- Eurostat Statistics Explained. Health in the European Union—facts and figures. http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Health_in_th... (2016). Accessed on 21 Dec 2016.
-
- Ferlay JSI, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray, F. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. http://globocan.iarc.fr/ (2013). Accessed on 21 Dec 2016.
-
- Struckmann V, Snoeijs S, Melchiorre MG, Hujala A, Rijken M, Quentin W, van Ginneken E. Caring for people with multiple chronic conditions in Europe. Eurohealth Incorporating Euro Obs. 2014;20(3):35–40. http://www.icare4eu.org/pdf/caring-for-people-with-multiple-chronic-cond.... Accessed on 21 Dec 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

