Influence of Prevalent and Incident Atrial Fibrillation on Post-Trial Major Events in ALLHAT
- PMID: 28987246
- PMCID: PMC5635839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnma.2017.02.005
Influence of Prevalent and Incident Atrial Fibrillation on Post-Trial Major Events in ALLHAT
Abstract
Aims: Limited information is available on long-term antihypertensive and lipid-lowering therapy effects on hypertensive patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter (AF/AFL) compared to those without. AF/AFL at baseline or during the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) (mean follow-up 4.9 years) markedly increased risk of stroke, heart failure, CHD, and all-cause mortality. We aimed to determine if AF/AFL continued to impact outcomes during post-trial follow-up (mean 3.8 years).
Methods: Patients were randomized to chlorthalidone, amlodipine, or lisinopril, and to pravastatin vs. usual care in the lipid-lowering trial (LLT). Of 31,473 available subjects, AF/AFL occurred in 854; 383/14,371 chlorthalidone (2.7%), 247/8565 amlodipine (2.9%), and 224/8537 lisinopril (2.6%). Post-hoc analyses utilized administrative databases for post-trial data. Individuals with AF/AFL were compared to those without during post-trial. Outcomes were analyzed by treatment groups for the antihypertensive and LLT trials.
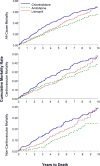
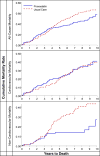
Results: Among 854 AF/AFL participants, 491 (57.5%) died: 220 in-trial, 271 post-trial. Ten-year all-cause mortality rates for those with in-trial AF/AFL were similar for chlorthalidone and lisinopril, but lower for amlodipine (68, 66, and 49 per 100 persons, respectively); adjusted HR for amlodipine vs. chlorthalidone was 0.68 (95% CI, 0.54-0.87). Ten-year all-cause mortality rates were 57 vs. 65 per 100 persons (pravastatin vs. usual care); non-CVD mortality rates, 18 vs. 39 per 100 persons (pravastatin vs. usual care) (adjusted HR = 0.46, 95% CI, 0.24-0.86).
Conclusion: Post-trial follow-up revealed continued deleterious AF/AFL effects. The amlodipine (ALLHAT) and pravastatin (ALLHAT-LLT) treatment groups showed lower all-cause and non-CVD mortality compared to the chlorthalidone and usual-care groups, respectively.
Keywords: Antihypertensive therapy; Atrial fibrillation; Heart failure; Stroke.
Copyright © 2017 National Medical Association. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
William Cushman reports grants from Eli Lilly, Boerhinger Ingelheim, and Merck. Drs. Davis and Piller report grants from NHLBI. All other authors have no financial interests to disclose. Jeffrey Cutler is a contractor for NHLBI; no specific funding was allocated for this work. The views expressed in this manuscript are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of NHLBI.
Figures

References
-
- Kannel WB, Abbott RD, Savage DD, McNamara PN. Epidemiologic features of chronic atrial fibrillation: The Framingham Study. N Eng J Med. 1982;306:1018–22. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Levy D, Vaziri SM, D’Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Wolf PA. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. JAMA. 1994;271:840–844. - PubMed
-
- Psaty BM, Manolio TA, Kuller LH, Kronmal RA, Cushman M, Fried LP, White R, Furberg CD, Rautaharju PM. Incidence of and risk factors for atrial fibrillation in older adults. Circulation. 1997;96(7):2155–2161. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, Singer DE. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults. National implications of rhythm management and stroke prevention; the Anticoagulation and Risk Factor in in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–5. - PubMed
-
- Estes NA, 3rd, Sacco RL, Al-Khatib SM, Ellinor PT, Bezanson J, Alonso A, Antzelevitch C, Brockman RG, Chen PS, Chugh SS, Curtis AB, DiMarco JP, Ellenbogen KA, Epstein AE, Ezekowitz MD, Fayad P, Gage BF, Go AS, Hlatky MA, Hylek EM, Jerosch-Herold M, Konstam MA, Lee R, Packer DL, Po SS, Prystowsky EN, Redline S, Rosenberg Y, Van Wagoner DR, Wood KA, Yue L, Benjamin EJ. American Heart Association atrial fibrillation research summit: a conference report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011 Jul 19;124(3):363–72. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

