Analysis of bioactive constituents from the leaves of Amorpha fruticosa L
- PMID: 28987377
- PMCID: PMC9328870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.10.006
Analysis of bioactive constituents from the leaves of Amorpha fruticosa L
Abstract
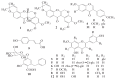
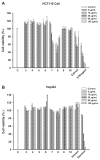
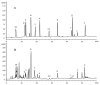
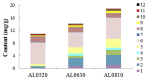
Amorpha fruticosa L. is a Chinese folk medicine and rich in polyphenols. Fifteen known compounds were isolated and identified from the leaves of A. fruticosa L. They are tephrosin (1), 6a,12a-dehydrodeguelin (2), vitexin (3), afrormosin-7-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (4), 2″-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl isovitexin (5), rutin (6), chrysoeriol (7), 7-O-methylluteolin (8), trans-p-coumaric acid (9), 2-benzyl-4,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid-4-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (10), formononetin (11), quercetin (12), apigenin (13), β-sitosterol (14), and β-daucosterol (15). Compounds 3, 4, 5, and 7-9 were isolated from A. fruticosa L. for the first time. Cytotoxicity of individual compounds 3-10 and 90% ethanol extract against human cancer cell lines HCT116 and HepG2 were reported. The results suggested that compounds 7 and 8, and the crude extract exhibited inhibitory effects on human cancer cell line HCT116, at concentrations of 100 μg/mL, 5 μg/mL, and 25 μg/mL at <60% of cell viability rate, respectively. In addition, a valid high-performance liquid chromatography diode array detector method was established to quantitatively analyze compounds 1-12 in the leaves of A. fruticosa L., which was harvested at three different stages of maturity from May 20 to August 10, 2014. The results demonstrated that contents were greatly influenced by the maturity. Total amounts of the analytical constituents gradually increased from May 20 to August 10, with the values ranging from 10.86 mg/g to 18.84 mg/g, whereas bioactive compounds 7 and 8 presented the opposite variation trend. The results of this study may provide data for further study and comprehensive utilization of A. fruticosa L.
Keywords: Amorpha fruticosa L.; Leguminosae; cytotoxicity; phenolics; quantitative analysis.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All contributing authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Phenolic Metabolites from the Fruits of Amorpha fruticosa.J Nat Prod. 2017 Jan 27;80(1):169-180. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00809. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Nat Prod. 2017. PMID: 28075580
-
Evaluation of anti-bacterial and wound healing activity of the fruits of Amorpha fruticosa L.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013 Apr 12;10(3):458-68. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v10i3.12. eCollection 2013. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 24146475 Free PMC article.
-
[Chemical constituents from leaves of Nelumbo nucifera].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Mar;38(5):703-8. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23724680 Chinese.
-
Amorpha fruticosa - A Noxious Invasive Alien Plant in Europe or a Medicinal Plant against Metabolic Disease?Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 8;8:333. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00333. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28642702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Woodfordia fruticosa (L.) Kurz: in vitro biotechnological interventions and perspectives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;107(19):5855-5871. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12695-x. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37522947 Review.
Cited by
-
Formononetin: A Review of Its Anticancer Potentials and Mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 26;10:820. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00820. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31402861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemodiversity and Antinociceptive Activity of Amorpha fruticosa L. Essential Oil.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 30;13(21):3045. doi: 10.3390/plants13213045. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39519963 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Study of Amorpha fruticosa WRKY20 Gene in Response to Drought Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 31;24(15):12231. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512231. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569607 Free PMC article.
-
Formononetin: a review of its source, pharmacology, drug combination, toxicity, derivatives, and drug delivery systems.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 3;16:1534798. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1534798. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40098623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formononetin: pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04247-z. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40488850 Review.
References
-
- Liu J, Wang ET, Chen WX. Diverse rhizobia associated with woody legumes Wisteria sinensis, Cercis racemosa and Amorpha fruticosa grown in the temperate zone of China. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2005;28:465–77. - PubMed
-
- Chinese PU. A dictionary of Chinese Materia Medica. 3rd ed. Beijing: Chinese Science and Technology Press of Medicine; 1997.
-
- Claisse J, Crombie L, Peace R. Structure and stereochemistry of the vicianoside amorphin, the first rotenoid glycoside. J Chem Soc. 1964:6023–36.
-
- Somleva T, Ognyanov I. New rotenoids in Amorpha fruticosa fruits. Planta Med. 1985;51:219–21.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
