Pathophysiology of the Effects of Alcohol Abuse on the Endocrine System
- PMID: 28988577
- PMCID: PMC5513689
Pathophysiology of the Effects of Alcohol Abuse on the Endocrine System
Abstract
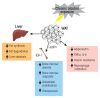
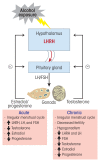
Alcohol can permeate virtually every organ and tissue in the body, resulting in tissue injury and organ dysfunction. Considerable evidence indicates that alcohol abuse results in clinical abnormalities of one of the body's most important systems, the endocrine system. This system ensures proper communication between various organs, also interfacing with the immune and nervous systems, and is essential for maintaining a constant internal environment. The endocrine system includes the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis, the hypothalamic-pituitary-growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis, and the hypothalamic-posterior pituitary axis, as well as other sources of hormones, such as the endocrine pancreas and endocrine adipose tissue. Alcohol abuse disrupts all of these systems and causes hormonal disturbances that may result in various disorders, such as stress intolerance, reproductive dysfunction, thyroid problems, immune abnormalities, and psychological and behavioral disorders. Studies in both humans and animal models have helped shed light on alcohol's effects on various components of the endocrine system and their consequences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ben-Jonathan N, Hnasko R. Dopamine as a prolactin (PRL) inhibitor. Endocrine Reviews. 2001;22(6):724–763. - PubMed
-
- De A, Boyadjieva N, Oomizu S, Sarkar DK. Ethanol induces hyperprolactinemia by increasing prolactin release and lactotrope growth in female rats. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2002;26(9):1420–1429. - PubMed
-
- De A, Boyadjieva N, Pastorcic M, Sarkar D. Potentiation of the mitogenic effect of estrogen on the pituitary-gland by alcohol-consumption. International Journal of Oncology. 1995;7(3):643–648. - PubMed
-
- Dees WL, Kozlowski GP. Differential effects of ethanol on luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone and prolactin secretion in the female rat. Alcohol. 1984;1(6):429–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

