Fluorinated phenmetrazine "legal highs" act as substrates for high-affinity monoamine transporters of the SLC6 family
- PMID: 28988906
- PMCID: PMC7294773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.10.006
Fluorinated phenmetrazine "legal highs" act as substrates for high-affinity monoamine transporters of the SLC6 family
Abstract
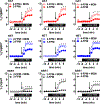
A variety of new psychoactive substances (NPS) are appearing in recreational drug markets worldwide. NPS are compounds that target various receptors and transporters in the central nervous system to achieve their psychoactive effects. Chemical modifications of existing drugs can generate NPS that are not controlled by current legislation, thereby providing legal alternatives to controlled substances such as cocaine or amphetamine. Recently, 3-fluorophenmetrazine (3-FPM), a derivative of the anorectic compound phenmetrazine, appeared on the recreational drug market and adverse clinical effects have been reported. Phenmetrazine is known to elevate extracellular monoamine concentrations by an amphetamine-like mechanism. Here we tested 3-FPM and its positional isomers, 2-FPM and 4-FPM, for their abilities to interact with plasma membrane monoamine transporters for dopamine (DAT), norepinephrine (NET) and serotonin (SERT). We found that 2-, 3- and 4-FPM inhibit uptake mediated by DAT and NET in HEK293 cells with potencies comparable to cocaine (IC50 values < 2.5 μM), but display less potent effects at SERT (IC50 values >80 μM). Experiments directed at identifying transporter-mediated reverse transport revealed that FPM isomers induce efflux via DAT, NET and SERT in HEK293 cells, and this effect is augmented by the Na+/H+ ionophore monensin. Each FPM evoked concentration-dependent release of monoamines from rat brain synaptosomes. Hence, this study reports for the first time the mode of action for 2-, 3- and 4-FPM and identifies these NPS as monoamine releasers with marked potency at catecholamine transporters implicated in abuse and addiction. This article is part of the Special Issue entitled 'Designer Drugs and Legal Highs.'
Keywords: Amphetamine; Legal high; Monoamine transporter; New psychoactive substances; Phenmetrazine.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
HHS has received honoraria for lectures and consulting from AbbVie, Lundbeck, MSD, Ratiopharm, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis and Serumwerk Bernburg (past 5 years). All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
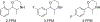
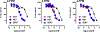
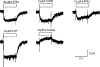
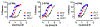
References
-
- BACKBERG M, WESTERBERGH J, BECK O & HELANDER A 2016. Adverse events related to the new psychoactive substance 3-fluorophenmetrazine - results from the Swedish STRIDA project. Clin Toxicol (Phila), 54, 819–825. - PubMed
-
- BAUMANN MH, PARTILLA JS, LEHNER KR, THORNDIKE EB, HOFFMAN AF, HOLY M, ROTHMAN RB, GOLDBERG SR, LUPICA CR, SITTE HH, BRANDT SD, TELLA SR, COZZI NV & SCHINDLER CW 2013. Powerful cocaine-like actions of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacology, 38, 552–62. - PMC - PubMed
Web- References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

