Plants' Natural Products as Alternative Promising Anti- Candida Drugs
- PMID: 28989245
- PMCID: PMC5628516
- DOI: 10.4103/phrev.phrev_8_17
Plants' Natural Products as Alternative Promising Anti- Candida Drugs
Abstract
Candida is a serious life-threatening pathogen, particularly with immunocompromised patients. Candida infections are considered as a major cause of morbidity and mortality in a broad range of immunocompromised patients. Candida infections are common in hospitalized patients and elderly people. The difficulty to eradicate Candida infections is owing to its unique switch between yeast and hyphae forms and more likely to biofilm formations that render resistance to antifungal therapy. Plants are known sources of natural medicines. Several plants show significant anti-Candida activities and some of them have lower minimum inhibitory concentration, making them promising candidates for anti-Candida therapy. However, none of these plant products is marketed for anti-Candida therapy because of lack of sufficient information about their efficacy, toxicity, and kinetics. This review revises major plants that have been tested for anti-Candida activities with recommendations for further use of some of these plants for more investigation and in vivo testing including the use of nanostructure lipid system.
Keywords: Anti-Candida; Candida; biofilm; natural products; plants.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
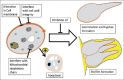

References
-
- d’Enfert C. Hidden killers: Persistence of opportunistic fungal pathogens in the human host. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009;12:358–64. - PubMed
-
- Rees JR, Pinner RW, Hajjeh RA, Brandt ME, Reingold AL. The epidemiological features of invasive mycotic infections in the San Francisco Bay area 1992-1993: Results of population-based laboratory active surveillance. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:1138–47. - PubMed
-
- Hamad M, Kazandji N, Awadallah S, Allam H. Prevalence and epidemiological characteristics of vaginal candidiasis in the UAE. Mycoses. 2014;57:184–90. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
