Skeletal Muscle CAP Expression Increases after Dietary Restriction and Aerobic Training in Women with a History of Gestational Diabetes
- PMID: 28989819
- PMCID: PMC5628746
- DOI: 10.4172/2167-7182.1000354
Skeletal Muscle CAP Expression Increases after Dietary Restriction and Aerobic Training in Women with a History of Gestational Diabetes
Abstract
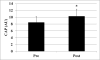
The purpose is to determine the effects of 6 months caloric restriction and aerobic training (3x/wk) (CR+AEX) on c-CBL associated protein (CAP) gene expression in women with a history of GDM. CAP is involved in cell signaling and protein ubiquitination, and is linked to the development of insulin resistance. Obese (BMI=32 ± 1 kg/m2, % fat=46 ± 2, X ± SEM), sedentary (VO2 max=21.2 ± 1.2 ml/kg/min), women aged 52 ± 2 years participated in 6 months D+WL (n=10) with body composition, fitness (VO2 max), and glucose tolerance testing. Insulin sensitivity was assessed during the last 30 min of 2-hour hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps (40 mU.m-2.min-1) pre and post interventions. Vastus lateralis skeletal muscle biopsies (n=7) were conducted and CAP, GLUT4 and glycogen synthase (GS) gene expression measured by RT-PCR. No change in FFM by DXA was observed, but body weight decreased 8% with losses of total body fat mass (P<0.05) and a 10% increase in VO2 max (P<0.01). Glucose and insulin areas under the curve by OGTT decreased (P<0.05). Glucose utilization during the clamp increased 27% (23.1 ± 3.8 vs. 29.4 ± 3.6 umol.kg.min-1, P<0.05). Vastus lateralis skeletal muscle CAP expression increased 21% (P<0.05) but GLUT4 did not. Results suggest that changes in CAP could be involved in the improvement in glucose metabolism with caloric restriction and aerobic training in women with a history of gestational diabetes.
Keywords: Aging; Exercise; Gestational diabetes; Insulin signaling; Nutrition; Obesity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improvements in insulin sensitivity after aerobic exercise and weight loss in older women with a history of gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Endocr Res. 2016 May;41(2):132-41. doi: 10.3109/07435800.2015.1094087. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Endocr Res. 2016. PMID: 26925596 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic exercise + weight loss decreases skeletal muscle myostatin expression and improves insulin sensitivity in older adults.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013 Jul;21(7):1350-6. doi: 10.1002/oby.20216. Epub 2013 May 19. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013. PMID: 23687104 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise with calorie restriction improves insulin sensitivity and glycogen synthase activity in obese postmenopausal women with impaired glucose tolerance.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jan 1;302(1):E145-52. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00618.2010. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22008454 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of aerobic and resistive exercise training on glucose disposal and skeletal muscle metabolism in older men.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006 May;61(5):480-7. doi: 10.1093/gerona/61.5.480. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006. PMID: 16720745
-
Insulin resistance with aging: effects of diet and exercise.Sports Med. 2000 Nov;30(5):327-46. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200030050-00002. Sports Med. 2000. PMID: 11103847 Review.
References
-
- Buchanan TA, Xiang A, Kjos SL, Lee WP, Trigo E, et al. Gestational diabetes: antepartum characteristics that predict postpartum glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes in Latino women. Diabetes. 1998;47:1302–1310. - PubMed
-
- Catalano PM, Bernstein IM, Wolfe RR, Srikanta S, Tyzbir E, et al. Subclinical abnormalities of glucose metabolism in subjects with previous gestational diabetes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986;155:1255–1262. - PubMed
-
- Ryan EA, Imes S, Liu D, McManus R, Finegood DT, et al. Defects in insulin secretion and action in women with a history of gestational diabetes. Diabetes. 1995;44:506–512. - PubMed
-
- Ward WK, Johnston CL, Beard JC, Benedetti TJ, Halter JB, et al. Insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion in subjects with histories of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1985;34:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Ward WK, Johnston CL, Beard JC, Benedetti TJ, Porte D. Abnormalities of islet B-cell function, insulin action, and fat distribution in women with histories of gestational diabetes: relationship to obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985;61:1039–1045. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous