Mechanism of the effect of saikosaponin on atherosclerosis in vitro is based on the MAPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 28990046
- PMCID: PMC5779967
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7691
Mechanism of the effect of saikosaponin on atherosclerosis in vitro is based on the MAPK signaling pathway
Abstract
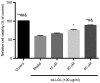
The present study aimed to investigate the effects of saikosaponin on oxidized low‑density lipoprotein (ox‑LDL)‑induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) injury and apoptosis, and examine the involvement of the mitogen‑activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. The viability and apoptosis of HUVECs were detected using an MTT assay and flow cytometry. ELISA analysis was applied to measure the levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)‑α and interleukin (IL)‑6 cytokines. Nuclear factor (NF)‑κB p65 nuclear translocation was observed using immunofluorescence staining. The levels of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule‑1 were detected using reverse transcription‑polymerase chain reaction analysis. The phosphorylation of B‑cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‑2), Bcl‑2‑associated X protein (Bax), caspase‑3 p38, c‑Jun N‑terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal‑regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 were detected using western blot analysis. The results revealed that saikosaponin increased the viability of the HUVECs and decreased the early‑stage apoptotic rate of the HUVECs induced by ox‑LDL. The expression levels of inflammatory cytokines in the injured vascular endothelial cells were decreased, the expression levels of adhesion molecules were reduced, the activity of superoxide dismutase was increased, and malondialdehyde content was decreased. Therefore, the inflammatory response and oxidative stress were inhibited. Simultaneously, the levels of Bcl‑2 increased, the levels of Bax and caspase‑3 decreased, and the nuclear translocation of NF‑κB p65 was significantly inhibited. The protein levels of phosphorylated p38 and JNK were reduced, whereas that of ERK1/2 remained unaffected. It was concluded that the MAPK signaling pathway mediated HUVEC injury induced by ox‑LDL. However, saikosaponin inhibited the HUVEC injury induced by ox‑LDL through inhibiting the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, and possibly also through the JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

