Estradiol‑enhanced osteogenesis of rat bone marrow stromal cells is associated with the JNK pathway
- PMID: 28990107
- PMCID: PMC5779911
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7699
Estradiol‑enhanced osteogenesis of rat bone marrow stromal cells is associated with the JNK pathway
Abstract
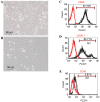
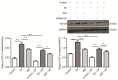
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) can differentiate into osteoblasts. The present study investigated the osteogenic effects of estradiol, as well as the role of the c‑Jun N‑terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway in promoting estradiol‑enhanced osteogenesis of rat (r)BMSCs. rBMSCs were treated for 7 days with or without estradiol and further treated with or without the JNK‑specific inhibitor SP600125. The role of estrogen during rBMSC osteogenesis was evaluated by alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralized nodule formation using the Gomori method and Alizarin red S staining, respectively. Subsequently, the mRNA expression levels of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF‑β1) and core‑binding factor α1 (Cbfα1) were evaluated by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and TGF‑β1, Cbfα1 and phosphorylated (p)‑JNK protein expression was detected by western blotting. All groups treated with SP600125 expressed low levels of TGF‑β1 and Cbfα1 mRNA and protein, and low p‑JNK protein expression. Compared with the control cells, rBMSCs cultured with estradiol exhibited a significant upregulation in the expression levels of osteogenic genes and proteins. The present study demonstrated that estradiol enhanced osteogenic differentiation of rBMSCs and that the JNK signaling pathway was involved in this process, providing insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in rBMSC osteogenesis upon estradiol stimulation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells by activating the ERα-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:931-939. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.107. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27764755
-
miR-214 suppresses the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and these effects are mediated through the inhibition of the JNK and p38 pathways.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Jan;39(1):71-80. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2826. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27959394 Free PMC article.
-
Irradiation alters the differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jan;13(1):213-23. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4539. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26572960 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 8 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells by inhibiting histone H3K9 acetylation and RUNX2 activity.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Sep;54:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25019367
-
[Effect of Biaxial Tensile Strain on Expression of Osteogenic Specificity Markers of Rat Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Vitro].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;33(3):499-505. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29709150 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Dihydrotestosterone and 17-Estradiol Enhancement of in vitro Osteogenic Differentiation of Castrated Male Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (rBMMSCs).Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2019 Oct 1;13(4):208-219. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31871596 Free PMC article.
-
17β-estradiol promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by regulating mitophagy through ARC.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jan 10;20(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05400-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39794817 Free PMC article.
-
miR-122 Exerts Inhibitory Effects on Osteoblast Proliferation/Differentiation in Osteoporosis by Activating the PCP4-Mediated JNK Pathway.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Jun 5;20:345-358. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.11.038. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32199130 Free PMC article.
-
JUN promotes chicken female differentiation by inhibiting Smad2.Cytotechnology. 2021 Feb;73(1):101-113. doi: 10.1007/s10616-020-00447-y. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Cytotechnology. 2021. PMID: 33505118 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of testosterone and 17β-estradiol on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation capacity of human bone-derived mesenchymal stromal cells of postmenopausal women.Bone Rep. 2019 Oct 21;11:100226. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2019.100226. eCollection 2019 Dec. Bone Rep. 2019. PMID: 31709277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siris ES, Miller PD, Barrett-Connor E, Faulkner KG, Wehren LE, Abbott TA, Berger ML, Santora AC, Sherwood LM. Identification and fracture outcomes of undiagnosed low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: Results from the National Osteoporosis Risk Assessment. JAMA. 2001;286:2815–2822. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.22.2815. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Rahbi B, Zakaria R, Othman Z, Hassan A, Ahmad AH. Enhancement of BDNF concentration and restoration of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis accompany reduced depressive-like behaviour in stressed ovariectomised rats treated with either Tualang honey or estrogen. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:310821. doi: 10.1155/2014/310821. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

