RUNX1: A Regulator of NF-kB Signaling in Pulmonary Diseases
- PMID: 28990531
- PMCID: PMC5876917
- DOI: 10.2174/1389203718666171009111835
RUNX1: A Regulator of NF-kB Signaling in Pulmonary Diseases
Abstract
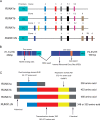
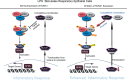
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1), a member of the RUNX family, is one of the key regulatory proteins in vertebrates. RUNX1 is involved in embryonic development, hematopoiesis, angiogenesis, tumorigenesis and immune response. In the past few decades, studies mainly focused on the effect of RUNX1 on acute leukemia and cancer. Only few studies about the function of RUNX1 in the pathological process of pulmonary diseases have been reported. Recent studies have demonstrated that RUNX1 is highly expressed in both mesenchymal and epithelial compartments of the developing and postnatal lung and that it plays a critical role in the lipopolysaccharide induced lung inflammation by regulating the NF-kB pathway. RUNX1 participates in the regulation of the NF-kB signaling pathway through interaction with IkB kinase complex in the cytoplasm or interaction with the NF-kB subunit P50. NF-kB is well-known signaling pathway necessary for inflammatory response in the lung. This review is to highlight the RUNX1 structure, isoforms and to present the mechanism that RUNX1 regulates NF-kB. This will illustrate the great potential role of RUNX1 in the inflammation signaling pathway in pulmonary diseases.
Keywords: IKK; NF-kB; P50; RUNX1; lung; pulmonary inflammation.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures
References
-
- Blyth K., Cameron E.R., Neil J.C. The RUNX genes: Gain or loss of function in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5(5):376–387. - PubMed
-
- De Braekeleer E., Douet-Guilbert N., Morel F., Le Bris M.J., Ferec C., De Braekeleer M. RUNX1 translocations and fusion genes in malignant hemopathies. Future Oncol. 2011;7(1):77–91. - PubMed
-
- Okuda T., van Deursen J., Hiebert S.W., Grosveld G., Downing J.R. AML1, the target of multiple chromosomal translocations in human leukemia, is essential for normal fetal liver hematopoiesis. Cell. 1996;84(2):321–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

