Triglycerides cross the blood-brain barrier and induce central leptin and insulin receptor resistance
- PMID: 28990588
- PMCID: PMC5880581
- DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2017.231
Triglycerides cross the blood-brain barrier and induce central leptin and insulin receptor resistance
Abstract
Objective: Resistance at the brain receptors for leptin and insulin has been associated with increased feeding, obesity and cognitive impairments. The causal agent for central resistance is unknown but could be derived from the blood. Here we postulate whether hypertriglyceridemia, the major dyslipidemia of the metabolic syndrome, could underlie central leptin and insulin resistance.
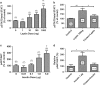
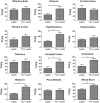
Design: We used radioactively labeled triglycerides to measure blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration, western blots to measure receptor activation, and feeding and cognitive tests to assess behavioral endpoints.
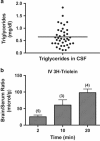
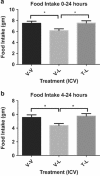
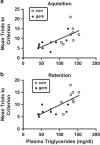
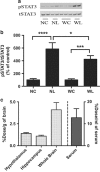
Results: Human CSF was determined to contain triglycerides, a finding previously unclear. The radioactive triglyceride triolein readily crossed the BBB and centrally administered triolein and peripherally administered lipids induced in vivo leptin and/or insulin resistance at hypothalamic receptors. Central triolein blocked the satiety effect of centrally administered leptin. Decreasing serum triglycerides with gemfibrozil improved both learning and memory inversely proportionate to triglyceride levels.
Conclusions: Triglycerides cross the blood-brain barrier rapidly, are found in human cerebrospinal fluid, and induce central leptin and insulin receptor resistance, decreasing satiety and cognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science (Washington DC) 1995; 269: 546–549. - PubMed
-
- Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D et al. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science (Washington DC) 1995; 269: 543–546. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, Jaspan JB, Maness LM. Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin. Peptides 1996; 17: 305–311. - PubMed
-
- Oomura Y, Hori N, Shiraishi T, Fukunaga K, Takeda H, Tsuji M et al. Leptin facilitates learning and memory performance and enhances hippocampal CA1 long-term potentiation and CaMK II phosphorylation in rats. Peptides 2006; 27: 2738–2749. - PubMed
-
- Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T et al. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science (Washington DC) 1995; 269: 540–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

