Disruption of calcineurin catalytic subunit (cnaA) in Epichloë festucae induces symbiotic defects and intrahyphal hyphae formation
- PMID: 28990722
- PMCID: PMC6638138
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12624
Disruption of calcineurin catalytic subunit (cnaA) in Epichloë festucae induces symbiotic defects and intrahyphal hyphae formation
Abstract
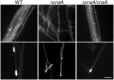
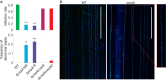
Calcineurin is a conserved calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase, consisting of a catalytic subunit A and a regulatory subunit B, which is involved in calcium-dependent signalling and regulation of various important cellular processes. In this study, we functionally characterized the catalytic subunit A (CnaA) of the endophytic fungus Epichloë festucae which forms a symbiotic association with the grass host Lolium perenne. We deleted the CnaA-encoding gene cnaA in E. festucae and examined its role in hyphal growth, cell wall integrity and symbiosis. This ΔcnaA strain had a severe growth defect with loss of radial growth and hyper-branched hyphae. Transmission electron microscopy and confocal microscopy analysis of the mutant revealed cell wall defects, aberrant septation and the formation of intrahyphal hyphae, both in culture and in planta. The mutant strain also showed a reduced infection rate in planta. The fluorescence of mutant hyphae stained with WGA-AF488 was reduced, indicating reduced chitin accessibility. Together, these results show that E. festucae CnaA is required for fungal growth, maintaining cell wall integrity and host colonization.
Keywords: CnaA; Epichloë; calcineurin; hyphal growth.
© 2017 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures






References
-
- Alshahni, M.M. , Shimizu, K. , Yoshimoto, M. , Yamada, T. , Nishiyama, Y. , Arai, T. and Makimura, K. (2016) Genetic and phenotypic analyses of calcineurin A subunit in Arthroderma vanbreuseghemii . Med. Mycol. 54, 207–218. - PubMed
-
- Becker, Y. , Eaton, C.J. , Brasell, E. , May, K.J. , Becker, M. , Hassing, B. , Cartwright, G.M. , Reinhold, L. and Scott, B. (2015) The fungal cell‐wall integrity MAPK cascade is crucial for hyphal network formation and maintenance of restrictive growth of Epichloë festucae in symbiosis with Lolium perenne . Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 28, 69–85. - PubMed
-
- Bowman, S.M. , Piwowar, A. , Al Dabbous, M. , Vierula, J. and Free, S.J. (2006) Mutational analysis of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor pathway demonstrates that GPI‐anchored proteins are required for cell wall biogenesis and normal hyphal growth in Neurospora crassa . Eukaryot. Cell, 5, 587–600. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

