Tracking individual action potentials throughout mammalian axonal arbors
- PMID: 28990925
- PMCID: PMC5633342
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.30198
Tracking individual action potentials throughout mammalian axonal arbors
Abstract
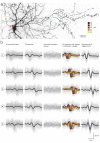
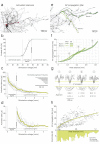
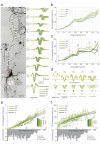
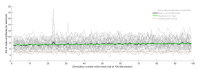
Axons are neuronal processes specialized for conduction of action potentials (APs). The timing and temporal precision of APs when they reach each of the synapses are fundamentally important for information processing in the brain. Due to small diameters of axons, direct recording of single AP transmission is challenging. Consequently, most knowledge about axonal conductance derives from modeling studies or indirect measurements. We demonstrate a method to noninvasively and directly record individual APs propagating along millimeter-length axonal arbors in cortical cultures with hundreds of microelectrodes at microsecond temporal resolution. We find that cortical axons conduct single APs with high temporal precision (~100 µs arrival time jitter per mm length) and reliability: in more than 8,000,000 recorded APs, we did not observe any conduction or branch-point failures. Upon high-frequency stimulation at 100 Hz, successive became slower, and their arrival time precision decreased by 20% and 12% for the 100th AP, respectively.
Keywords: HD-MEA; axonal physiology; electrode-neuron interface; neuroscience; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures




References
-
- Antic S, Major G, Zecevic D. Fast optical recordings of membrane potential changes from dendrites of pyramidal neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1999;82:1615–1621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

